Figure 1.
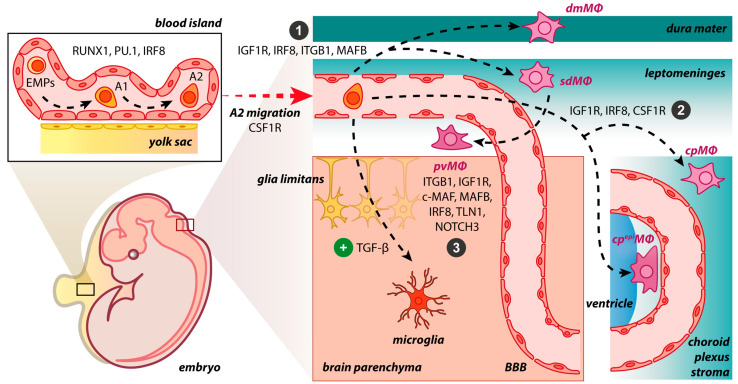
BAM origin and propagation in the developing mouse brain. The early differentiation of macrophage progenitors is regulated by the expression of RUNX1, PU.1, and IRF8 in the yolk sac, where the primitive erythro-myeloid progenitors (EMPs) give rise to CD45+ c-kitlo CX3CR1− immature (A1) cells and subsequently to CD45+ c-kit− CX3CR1+ (A2) cells. In the presence of TGF-β, A2 cells initiate a microgliogenesis program upon settlement in the brain parenchyma. In the absence of the TGF-β, A2 cells do not enter the brain parenchyma, populate the abutting connective tissue, and may follow distinct developmental pathways: (1) IGF1R, IRF8, ITGB1, and MAFB restrict progenitors to the meninges, either dura or the subdural mesenchymal niche; (2) IGF1R, IRF8, and CSF1R dictate progenitors’ residency within the choroid plexus; (3) ITGB1, IGF1R, c-MAF, MAFB, IRF8, TLN1, and NOTCH3 stimulate pvΜΦ generation postnatally from sdΜΦ. However, it is not yet fully understood if the dmΜΦ share common progenitors and drivers with sdΜΦ during embryogenesis. dmΜΦ: dural macrophages; sdΜΦ: subdural macrophages; pvΜΦ: perivascular macrophages; cpΜΦ: stromal choroid plexus macrophages; cpepiΜΦ: choroid epiplexus macrophages; BBB: blood–brain barrier.