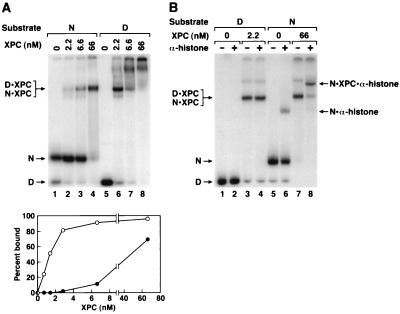
FIG. 5.
(A) Binding of XPC to nucleosomal DNA. XPC was incubated with naked DNA (D) or nucleosomes (N) and DNA-protein complexes were separated on a 5% nondenaturing gel. (Top) Autoradiogram; (Bottom) quantitative analysis of the binding data. The data points for lower concentrations of XPC were obtained from a separate experiment. The main retarded bands with either naked DNA or nucleosomes comigrate. With naked DNA high XPC concentrations led to multiple protein binding and a smear extending all the way to the origin. (B) Characterization of XPC-nucleosome complexes with an antihistone antibody. To the XPC-DNA and XPC-nucleosome reaction mixtures antihistone monoclonal antibodies were added where indicated, and the DNA-protein complexes were separated on a 4% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel. The nucleosome-XPC (N · XPC), nucleosome-XPC-antihistone antibody (N · XPC · α-histone), and DNA-XPC (D · XPC) bands are indicated. Note that at a high antibody concentration there was nonspecific binding of the antibody to DNA and hence in the supershift experiments less-than-saturating amounts of antibody were used, resulting in supershift of only a fraction of the histone-containing complexes (lanes 6 and 8).