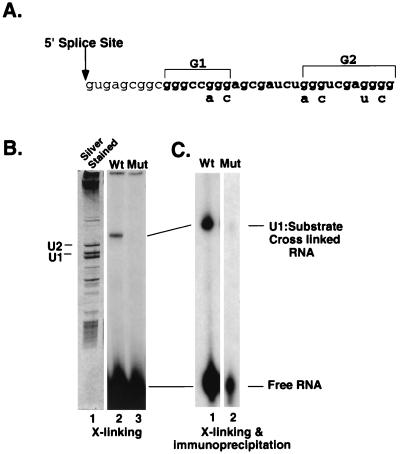
FIG. 3.
U1 snRNA binds to GGG enhancer elements in the human alpha-globin intron. (A) Sequence of the alpha-globin intron 2 5′ splice site and adjacent G1 and G2 intron elements. The sequence of the short alpha-globin wild-type G1-G2 RNA used for psoralen cross-linking is 5′ GGGCCGGGAGCGAUCUGGGUCGAGGGGG 3′. The mutant G1-G2 RNA sequence is 5′ GGGCCAGCAGCGAUCUAGCUCGAUGCG 3′. (B) Psoralen cross(X)-linking reactions using the wild-type (Wt) or mutant (Mut) 32P-labeled G1-G2 RNA were prepared as described in Materials and Methods and were analyzed on an 8% polyacrylamide–8.3 M urea denaturing gel. The gel was silver stained to identify nuclear RNAs (lane 1), and 32P-labeled G1-G2 RNA was visualized by autoradiography (lanes 2 and 3). The positions of the U1 and U2 snRNAs, free G1-G2 RNA, and the cross-linked species are indicated. (C) Psoralen cross-linking reactions were analyzed by immunoprecipitation with an anti-U1 70K antibody. RNAs precipitated by this antibody were separated on a 5% polyacrylamide–8.3 M urea denaturing gel and visualized by autoradiography. The film in panel B was exposed overnight, while that in panel C was exposed for 7 days.