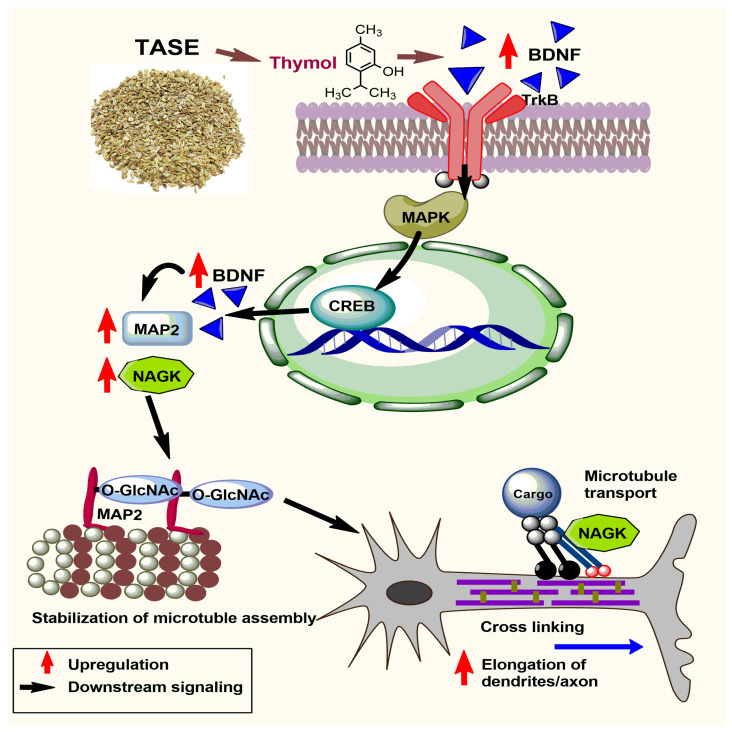
Figure 9.
Mechanism of TASE and thymol supplementation in neuronal differentiation and outgrowth effect. TASE and thymol supplementation upregulate the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which follows the TrkB-mediated downstream signaling pathway. Mitogen-activated protein kinase protein (MAPK) is phosphorylated, leading to upregulation of cyclic AMP-responsive element binding protein (CREB) family. CREB family of transcription factors upregulates microtubule-associated protein (MAP2) synthesis. Meanwhile, thymol also upregulates N-acetylglucosamine kinase, which is an enzyme of hexosamine biosynthetic pathway (HBP) which eventually upregulates the synthesis of O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNac). Addition of O-GlcNac using O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) promotes stabilization of MAP2-regulated microtubule assembly. Moreover, MAP2 proteins with modified serine or threonine residues close to phosphorylation sites might be prone to O-GlcNac modification. Cross-linking of microtubules is significantly upregulated, along with NAGK-mediated cargo transport mechanism on the microtubule, finally leading to rapid elongation of dendrites and axons.