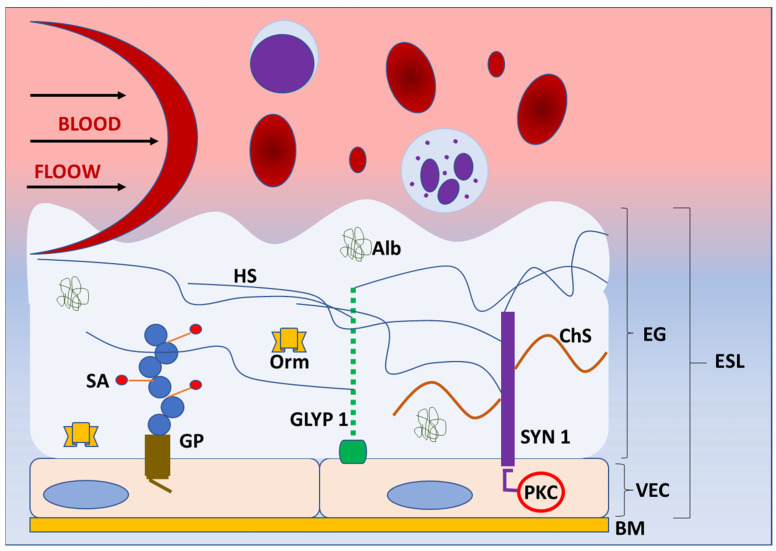
Figure 1.
Structure of endothelial glycoaylyx. Schematic representation of the basic structure of endothelial glycocalyx (EG) under normal physiologycal conditions. EG forms a protective layer of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans (syndecans, glypicans) and incorporated proteins on the luminal side of vascular endothelial cells, preventing direct contact of blood elements with the blood vessel wall. The components of EG transmit intraluminal events to endothelial cells activating the enzymes (protein kinase C) and intracellular signaling pathways. Abbreviations: Alb—albumin, BM—basement membrane, ChS—chondroitin sulphate, EG—endothelial glycocalyx, ESL—endothelial surphace layer, GLYP 1—glypican 1, GP—glycoprotein, HS—heparan sulphate, Orm—orosomucoid, PKC—protein kinase C, SA—sialic acid, SYN 1—syndecan 1, VEC—vascular endothelial cell.