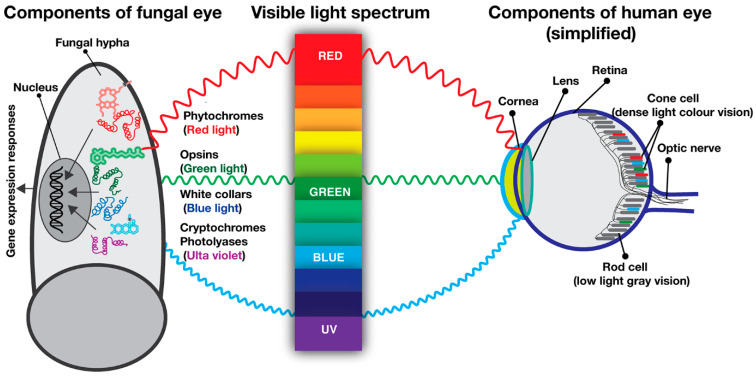
Figure 2.
A simplified comparative depiction of main light receptors in fungi versus vertebrate (human) photoreceptor cells within the retina. A fungal cell contains three sets of light receptors, red light receptors (phytochromes), green light receptors (opsins) and blue light receptors (White Collars, vivid, cryptochromes and photolyases). Chromophores (accessory molecules) help the light receptors to capture light waves. The inner layer of the human eye, retina, contains roughly 100 million photoreceptor cells, 95% of which belong to rod cells (providing grey vision) and 4–5% belong to cone cells (providing colour vision). Rod and cone cells transmit the signals to a vision centre in the brain via optic nerves.