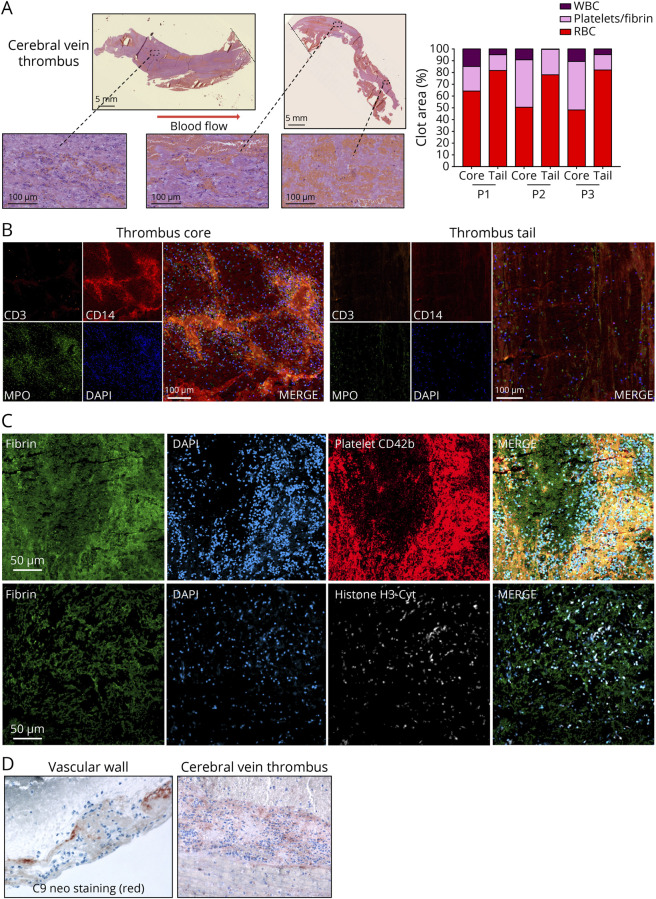
Figure 1. Histologic Characterization of VITT Cerebral Vein Thrombi.
(A) Hematoxylin-eosin-safran (HES) staining of cerebral vein thrombus of the representative patient 3, and quantification of the composition of the core and the tail of the thrombi from the 3 patients (P1–P3) using Orbit Image Analysis. (B) Confocal microscopy of the core and the tail of a cerebral vein thrombus with staining for T cells (Cluster of differentiation (CD)3), monocytes/macrophages (CD14), granulocytes (myeloperoxidase, MPO), and nucleated cells (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, DAPI). (C) Confocal microscopy of the core part of a cerebral vein thrombus with immunofluorescence labeling for fibrin, nucleated cells (DAPI), platelets (CD42b), and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) (anticitrullinated histone H3 antibody, H3-Cyt). (D) Complement activation (C9neo) staining in the vascular wall and in a cerebral vein thrombus. Representative images are shown. VITT = vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia.