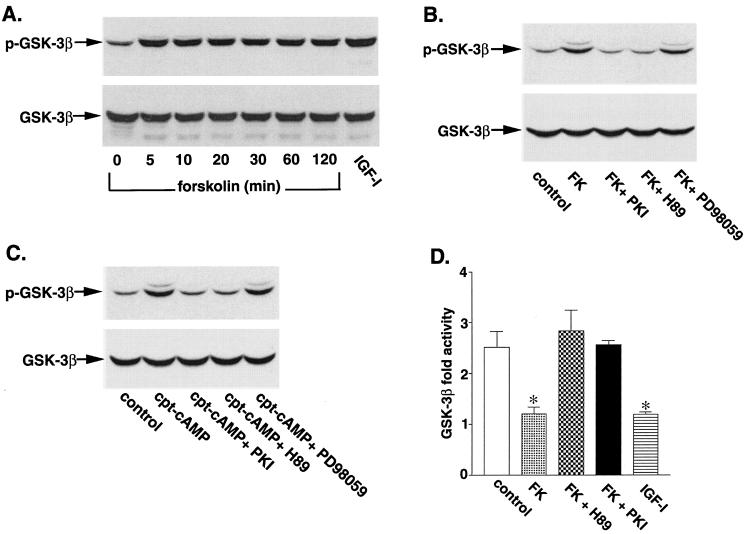
FIG. 1.
Phosphorylation and inhibition of GSK-3β by forskolin and CPT-cAMP. (A) Cerebellar granule neurons were cultured for 7 days, washed twice with BME, and then placed in serum-free medium containing 5 mM KCl. Two hours later, the cells were either left untreated or treated with 10 μM forskolin for the indicated times. Some neurons were incubated with IGF-I (50 ng/ml) for 30 min as a positive control. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with a phosphospecific GSK-3β (Ser9) antibody. (B) Neurons were pretreated for 30 min in the absence or presence of 25 μM cell-permeative PKI inhibitor, 10 μM H-89, or 30 μM PD98059 prior to incubation with 10 μM forskolin (FK) for 30 min. Cell lysates were immunoblotted with anti-GSK-3β (Ser9) antibody. (C) Neurons were pretreated for 30 min in the absence or presence of 25 μM cell-permeative PKI inhibitor, 10 μM H-89, or 30 μM PD98059 prior to incubation with 30 μM CPT-cAMP (cpt-cAMP) for 30 min. Results shown are representative of at least three experiments. (D) After serum and 25 mM KCl starvation in 5 mM KCl medium, neurons were incubated for 30 min with 10 μM forskolin in the presence or absence of 10 μM H-89, 25 μM PKI inhibitor, or IGF-I (50 ng/ml). After incubation, the neurons were lysed, GSK-3β was immunoprecipitated, and its activity was determined as described in Materials and Methods. Control neurons were washed similarly and then placed in serum-containing conditioned medium. The results are expressed as fold activity of control neurons and are mean values ± SEMs from three experiments. *, statistical significance according to Student's t test (P < 0.05 versus the value for 5 mM KCl).