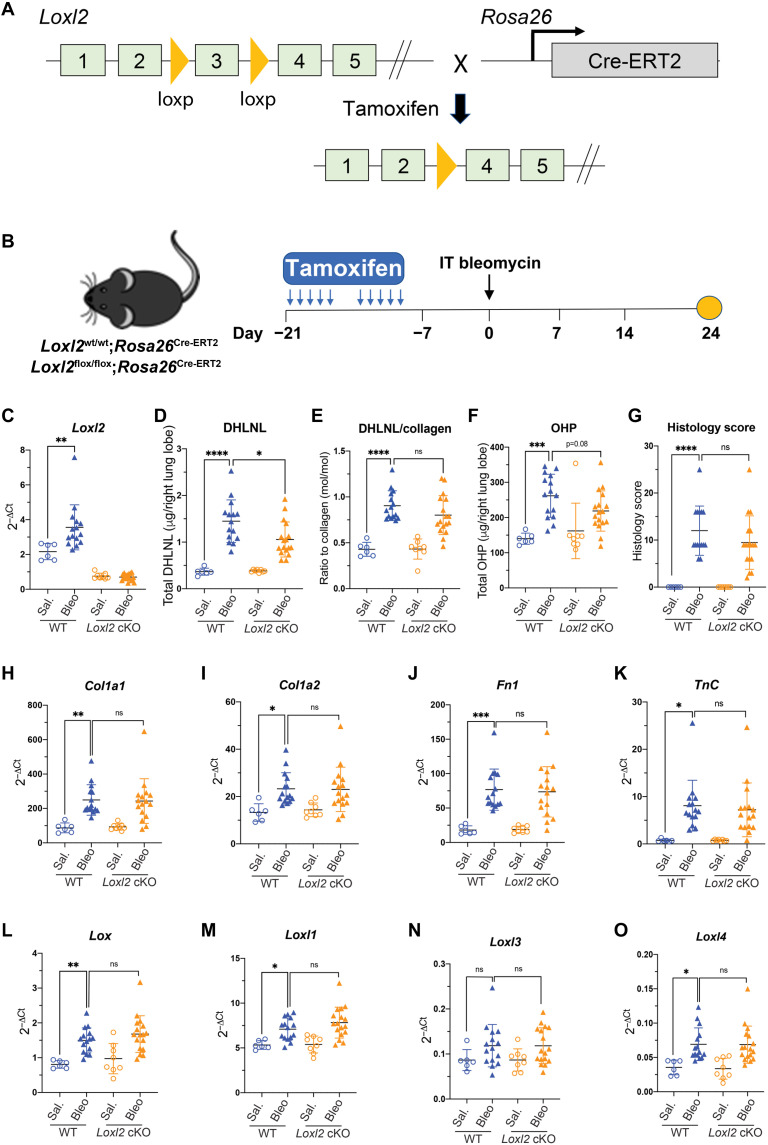
Fig. 3. LOXL2 modestly contributes to pathological collagen cross-linking but not fibrosis in the bleomycin model.
(A) Schematic conditional Loxl2 targeting. The exon 3 of Loxl2 gene has been flanked by loxP site. The Loxl2flox/flox mice breed with Rosa26Cre-ERT2 mice to generate Loxl2 cKO mice (Loxl2flox/flox; Rosa26Cre-ERT2) where Cre promoted recombination can be induced by tamoxifen. (B) Schematic regime of tamoxifen-induced Loxl2 deletion followed by intratracheal bleomycin challenge. Lungs were harvested for terminal analyses on day 24 after bleomycin challenge. (C) mRNA expression shows the efficient deletion of Loxl2 in the lungs from cKO mice. (D and E) Quantification of lung collagen cross-linking by (D) total DHLNL and (E) DHLNL normalized by collagen. (F and G) Quantification of lung fibrosis by (F) total OHP and (G) histology score. (H to K) mRNA expression of selective profibrotic genes from lung tissue. (L to O) mRNA expression of Lox family members from lung tissue. WT: saline, n = 6; bleomycin, n = 15; Loxl2 cKO: saline, n = 8; bleomycin, n = 17. Data represent means ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ****P < 0.0001. P value is calculated using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). ns, not significant.