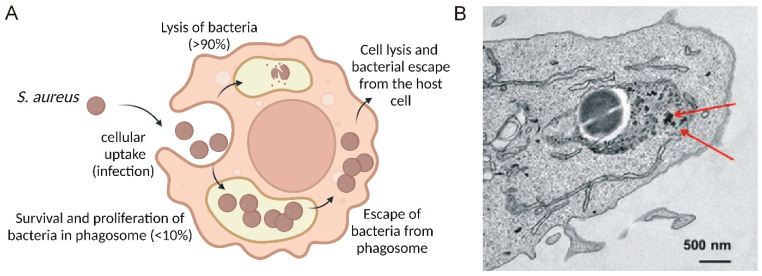
Figure 2.
MOF-mediated intracellular delivery of antibacterial agents for the treatment of MRSA. (A) The infectious cycle of MRSA in phagocytic cells. Only a minor part of the engulfed bacteria avoids dying in the phagolysosomal compartment due to multiple mechanisms. Further propagation of the pathogen in the vesicular compartment and cytosol eventually leads to lysis of the host cell and bacteria escape. (B) MOF-based nanomedicines can accumulate in the vesicular compartment containing the pathogen. TEM image represents MIL-100(Fe) nanoMOFs co-localized with S. aureus in J774 macrophages after 1-h incubation (red arrows). The figure adapted with permission from Wiley (ref. [75]).