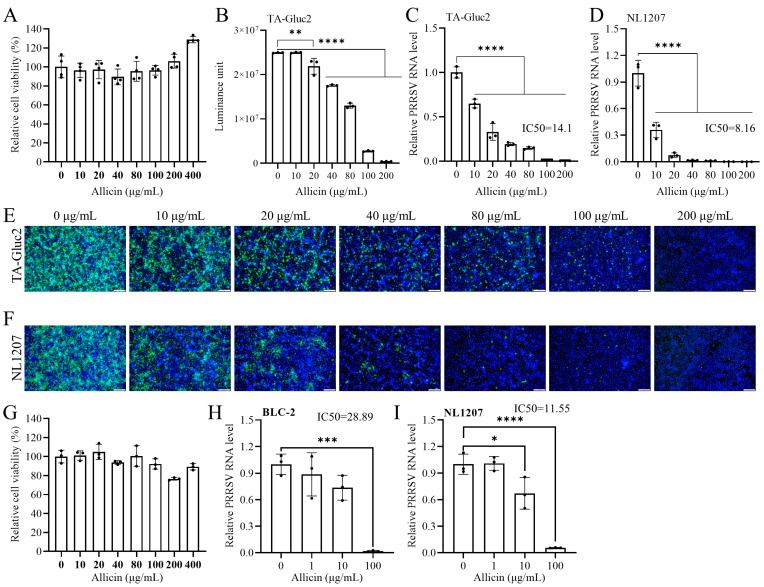
Figure 1.
The anti-PRRSV activity of allicin in MARC-145 cells and PAM. (A) The cytotoxicity of allicin on MARC-145 cells. MARC-145 cells were treated with allicin at various doses ranging from 0 μg/mL to 400 μg/mL for 24 h. The cytotoxicity of allicin was determined using a CCK-8 assay. (B) Allicin inhibited TA-Gluc2 infection in a dose-dependent manner. MARC-145 cells were infected with the TA-Gluc2 reporter virus at a dose of 1 MOI. At 24 hpi, culture supernatants were harvested for the gaussia luciferase assay. (C,D) MARC-145 cells were infected with TA-Gluc2 or NL1207 at a dose of 1 MOI in the presence of allicin at different concentrations (0, 10, 20, 40, 80, 100, 200, and 400 μg/mL) for 24 h. Viral loads in culture supernatants were determined by qRT-PCR targeting PRRSV ORF6. PRRSV infection was also monitored by IFA detection of PRRSV N in virus-infected cells, and cell nuclei were counterstained with DPAI (E,F). (G) The cytotoxicity of Allicin on PAMs. PAMs were incubated with allicin at various doses ranging from 0 to 100 μg/mL for 24 h. A CCK-8 assay was performed to examine the effect of allicin on the viability of PAM. (H,I) PAMs were infected with BLC-2 or NL1207 at a dose of 1 MOI in the presence of allicin at different concentrations (0, 1, 10, and 100 μg/mL) for 24 h. Viral loads in culture supernatants were determined by qRT-PCR targeting PRRSV ORF6. *, p-value < 0.05; **, p-value < 0.01; ***, p-value < 0.001; ****, p-value < 0.0001.