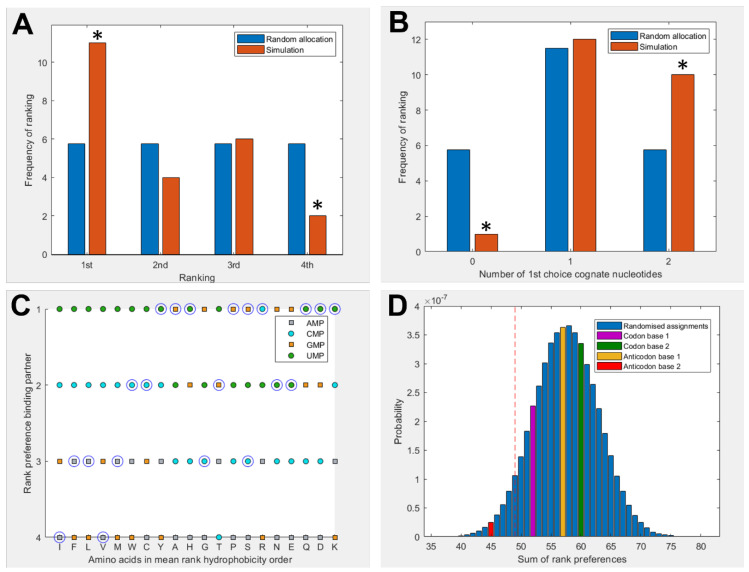
Figure 2.
(A) Rank preference of the anticodonic middle-base nucleotide for each the 20 amino acids as predicted by MD simulations. Included are 3 additional cognate assignments for hexacodonic amino acids (arginine, serine, and leucine), giving 23 allocations. Random allocation shows equal chance of each amino acid interacting most strongly with any nucleotide. (B) Number of amino acids predicted to interact most strongly with both, 1, or no nucleotides cognate at the 1st or 2nd position of the anticodon or codon, compared with random allocations. (C) Rank preference of each amino acid for each nucleotide, ordered by mean hydrophobicity rank of amino acids [8,80]. The correct middle base for each amino acid is circled. The three hexacodonic amino acids are each circled twice, but for arginine and leucine, the two different codons share the same middle base, so the circles are overlaid (giving eleven correct predictions). Circular datapoints show pyrimidines; square datapoints are purines. Green is UMP, blue CMP, orange GMP, and grey AMP. (D) Sum of rank preferences of the amino acids for their cognate nucleotides compared to randomised preferences. Highlighted bars are scores for: codon base 1 (purple), codon base 2 (green), anticodon base 1 (yellow), anticodon base 2 (red). All nucleotides are in the −1 charge state in all panels, and interactions are given with respect to ring nitrogens. Asterisks indicate statistically significant deviation from the null distribution at the 5% level.