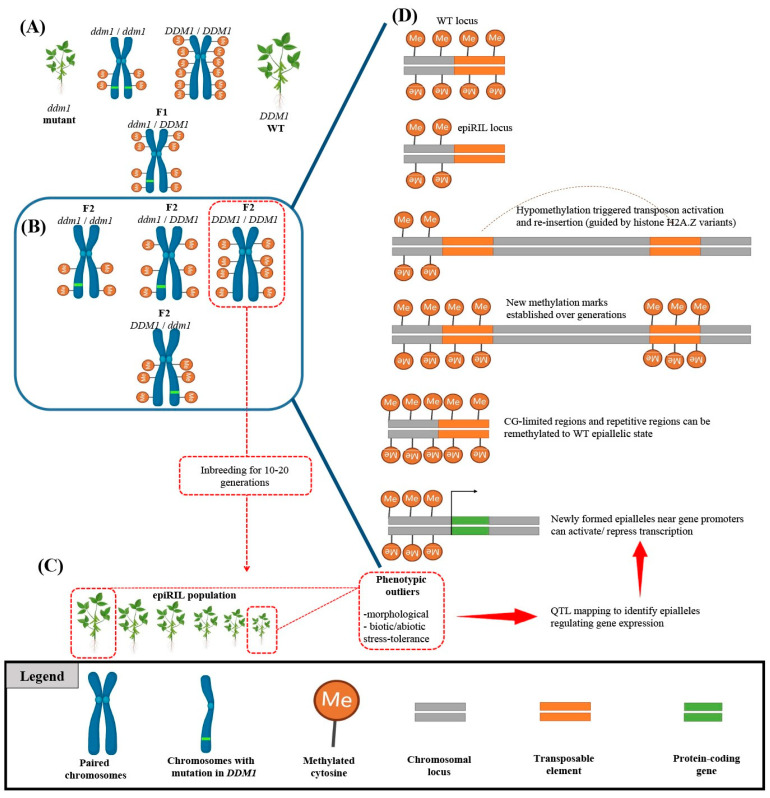
Figure 2.
Identification of novel epialleles using epigenetic recombinant inbred line (epiRIL) generation. (A) Crossing wild-type (WT) plants with DNA methylation-deficient mutants such as ddm1 mutant can redistribute genome-wide methylation patterns. (B) Progeny carrying WT alleles are selected for multigenerational inbreeding to generate epigenetic recombinant inbred lines (epiRILs). (C) The epiRIL population is evaluated for variations in stress resistance or morphological traits to identify phenotypic outliers. (D) The identified epiRIL lines undergo an epigenetic quantitative trait loci (epiQTL) analysis to discover novel epialleles. Such epialleles can occur due to the activation of transposable elements (TEs) and their reinsertion into distant loci, determined by chromatin properties and the nature of the target sequence (CG content). The scheme was adapted from Srikant and Tri Wibowo [115] and was created by using BioRender.com.