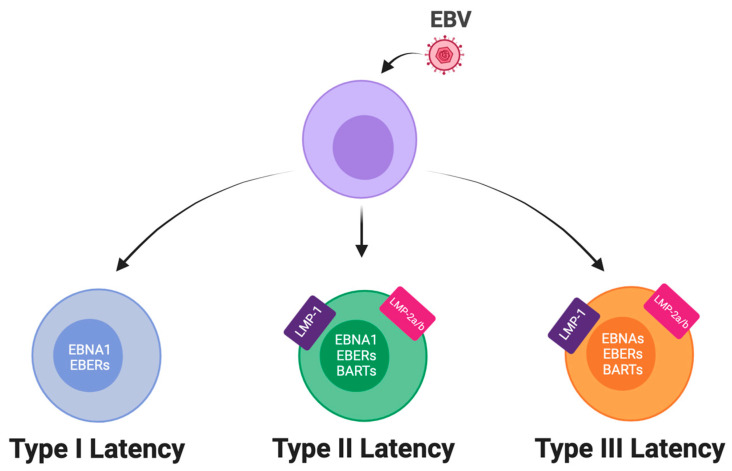
Figure 2.
Schematic view of the different latency types. Upon infection, EBV is able to establish latent infection in the host cell. The three main types of latency are depicted in this image. From the left: Type I latency is characterized by the expression of only the viral nuclear protein EBNA1 and the noncoding microRNAs EBERs; Type II latency involves the expression of EBNA1, EBERs, BARTs and the three transmembrane proteins LMP1, 2a, 2b. Type III latency is characterized by the expression of all the previously mentioned genes and the viral transcription factors EBNA2, EBNA3A, EBNA3B, EBNA3C, and EBNA-LP. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 2 April 2023).