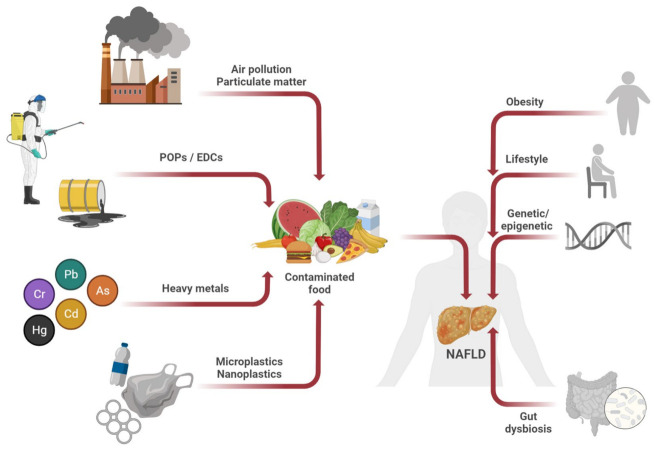
Figure 1.
In addition to obesity, lifestyle, genetic and epigenetic factors, and gut microbiota dysbiosis, dietary intake of several environmental pollutants, including persistent organic pollutants (POPs), endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs), heavy metals, micro- and nanoplastics promotes NAFLD development and progression. In addition to ingestion, exposure to air particulate matter through inhalation can be another risk factor for developing NAFLD, especially in the context of high urbanization due to the combination with other risk factors, including obesogenic food environment. Figure created with BioRender (https://biorender.com/, accessed on 11 April 2023).