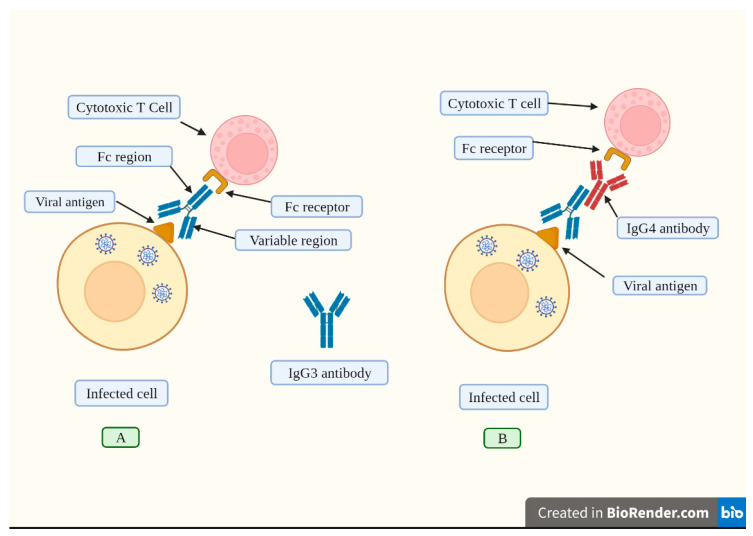
Figure 4.
An effective humoral response induced by vaccination consists of the synthesis of high IgG3 concentrations. (A). IgG3 antibodies attach to viral antigens exposed on infected cells’ membranes through its variable region. This antibody has a constant region (Fc) that is recognized by the corresponding receptor found on cytotoxic T cells and other immune cells. The cytotoxic T cell becomes activated and releases chemical agents that destroy the infected cell. (B). Repeated vaccination induces high IgG4 levels (depicted in red). This antibody inhibits the attachment of the Fc region from the IgG3 antibody to its receptor located on cytotoxic T cells, thus blocking its activation, and consequently, the infected cell is not destroyed. In this sense, repeated boosting causes a switch to the production of high IgG4 levels, which impair immune responses. Created with Biorender.