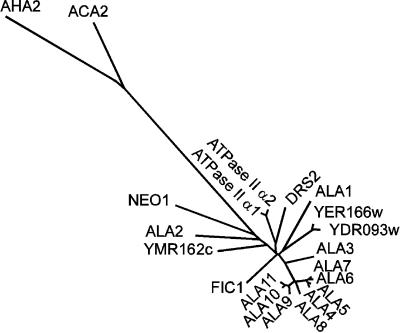
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic Tree of Conserved Sequence Segments of Selected P-Type ATPases.
The sequences are as follows. Type P4 ATPases: ALA1 to ALA11 (see Table 1 for accession numbers), Arabidopsis thaliana; YER166w (P32660), Saccharomyces cerevisiae; YDR093w (Q12675), S. cerevisiae; DRS2 (P39524), S. cerevisiae; ATPase II α1 (Q29449), Bos taurus; ATPase II α2 (Q9Y2Q0), Homo sapiens; FIC1 (O43520), H. sapiens; YMR162c (Q12674), S. cerevisiae; and NEO1 (P40527), S. cerevisiae. Type P2B ATPases: autoinhibited Ca2+-ATPase ACA2 (O81108), A. thaliana. Type P2A ATPases: endoplasmic reticulum–type Ca2+-ATPase (O04987), A. thaliana. Type P3A ATPases: plasma membrane H+-ATPase AHA2 (P19456), A. thaliana. The tree is based on the Fitch–Margoliash and least-squares method (PHYLIP; Felsenstein, 1989). The conserved segments used in the analysis are defined in Axelsen and Palmgren (1998).