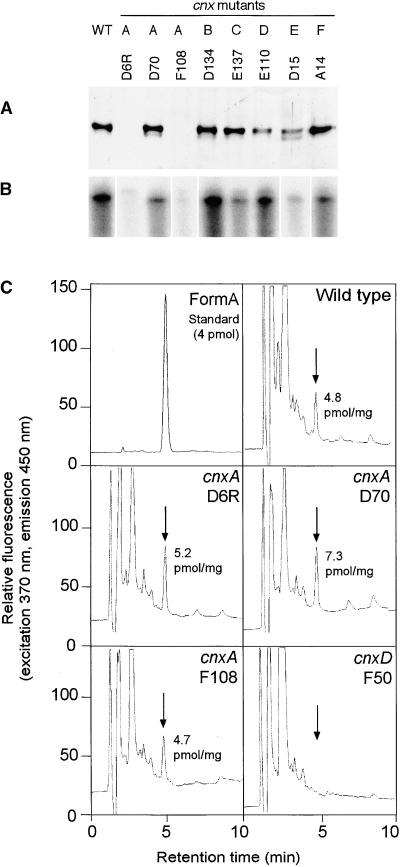
Figure 5.
Biochemical Characterization of Moco-Deficient Mutants from N. plumbaginifolia.
(A) Expression of Cnx1 in Moco-deficient mutants cnxA to cnxF. Shown is protein gel blot analysis of crude protein extracts from callus cultures of wild-type (WT) and mutant lines cnxA to cnxF (A to F). Equivalent amounts of total protein (50 μg) were loaded onto a 7.5% SDS–polyacrylamide gel, immunoblotted, and detected with polyclonal Cnx1 antibodies (Ak90cnx1; 1:2000 dilution).
(B) RNase protection assay of total RNA preparations (50 μg) of wild-type and mutant lines cnxA to cnxF. A 0.5-kb fragment encoding for the Cnx1 G domain was used as labeled antisense RNA probe (106 cpm of 32P), hybridized with total RNA, digested, separated on a 5% acrylamide gel, and exposed to radiographic film.
(C) Analysis of MPT/Moco in N. plumbaginifolia wild-type and mutant lines of cnxA and cnxD. Crude protein extracts of N. plumbaginifolia callus were oxidized with I2/KI to generate FormA-phospho from Moco and MPT. After dephosphorylation, FormA was purified further on QAE–Sephadex columns and analyzed by C18 reversed-phase HPLC with fluorescence detection. Shown is the elution profile of 4 pmol of FormA standard prepared from bovine xanthine oxidase. Arrows indicate the elution time of FormA in each chromatogram. The amount of MPT (per milligram of total protein) in the extract is given in each chromatogram.