Figure 9.
Cnx1 Generates Active Moco from Prebound MPT in the Absence of External Molybdate.
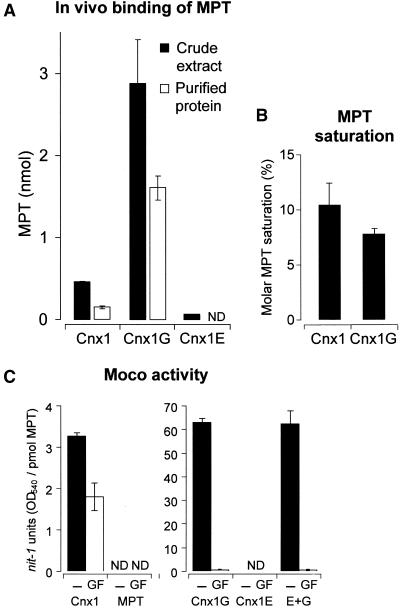
(A) Copurification of MPT with Cnx1 and its domains after recombinant expression in E. coli mogA RK5206 mutant. Cnx1 and the E and G domains were purified on small columns of nickel–trinitriloacetic acid matrix; minimal volumes of washing buffers were used to reduce dissociation of the bound MPT/Moco from the proteins. Shown are the total MPT content in crude extracts (black bars) and the total amount of MPT present in the purified protein fraction (white bars); the latter is called copurified MPT. Average values for MPT crude extracts are derived from triplicate purifications. The MPT values and standard deviations for copurified MPT were calculated from the percentage of MPT values for each purification in relation to the corresponding crude extract.
(B) Molar saturation of purified Cnx1 and G domains with copurified MPT. The data shown in (A) were correlated with the amount of purified protein (data not shown) and expressed as the percentage ratio of picomoles of MPT bound per picomole of protein.
(C) nit-1 reconstitutions of either the nit-1 crude extract (−) or the protein fraction of gel-filtrated nit-1 extract (GF) in the absence of external molybdate, as done with MPT bound to Cnx1, to G and E domains, or to an equimolar mixture of E and G domain (E+G), or with free MPT isolated from xanthine oxidase. The activity is given in nit-1-NR units per picomole of MPT. Standard errors were calculated from three different reconstitutions with at least three different MPT concentrations chosen from the linear range of the reconstitution assay.
ND, not detectable.