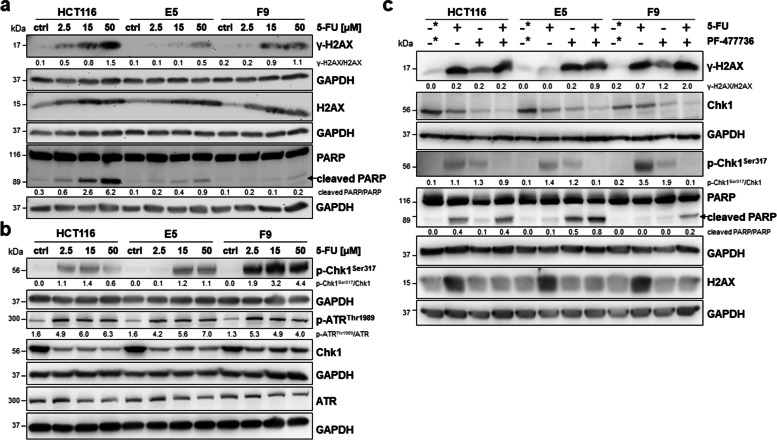
Fig. 2.
Activation of the ATR/Chk1 pathway plays an important role in ATF2-mediated 5-FU resistance. a Representative Western blotting for DNA damage marker γ-H2AX, total H2AX and apoptosis marker PARP after 5-FU treatment of HCT116 and HCT116 ATF2-KO clones E5 and F9 with different doses (2.5 µM, 15 µM, and 50 µM); ctrl: 24 h nontreated cells for control, GAPDH was used as loading control. Band intensities were quantified using ImageJ analysis software, and ratios were calculated against the GAPDH band intensity. For cleaved PARP, given ratios were calculated as cleaved PARP versus noncleaved PARP (ImageJ) and multiplied by 10 for visual reasons. b Representative Western blotting for DDR markers p-ATRThr1989, total ATR, p-Chk1.Ser317, and total Chk1 after 5-FU treatment of HCT116 and HCT116 ATF2-KO clones E5 and F9 with different doses (2.5 µM, 15 µM, and 50 µM); ctrl: 24 h nontreated cells for control, GAPDH was used as loading control. Band intensities were quantified using ImageJ analysis software, and ratios were calculated against the GAPDH band intensity. c Representative Western blotting after pretreating HCT116 and HCT116 ATF2-KO clones E5 and F9 with the Chk1 inhibitor PF-00477736 (1.65 nM) for 1 h followed by 5-FU (15 µM) for 48 h; 48 h DMSO-treated cells were used as control (-*), GAPDH was used as loading control. Band intensities were quantified using ImageJ analysis software, and ratios were calculated against the GAPDH band intensity. For cleaved PARP, given ratios were calculated as cleaved PARP versus noncleaved PARP (ImageJ)