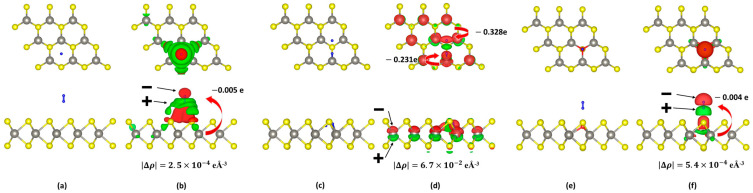
Figure 8.
Most stable adsorbed systems for each monolayer. Top and side views of hydrogen adsorbed (a) on the defect-free WS2 monolayer (Figure 2a), (c) on the defect-containing WS2 monolayer (Figure 2b), and (e) on the oxygen-containing WS2 monolayer (Figure 2c). Panels (b,d,f) show those charge density differences after adsorption as isodensity surfaces. Red indicates a negative charge difference (i.e., an increase in electron density) and green indicates a positive value with each of the absolute isosurface values of (b) 2.5 × 10−4 eÅ−3, (d) 6.7 × 10−2 eÅ−3, and (f) 5.4 × 10−4 eÅ−3. The values of the charge transfer are indicated by the red arrows, respectively.