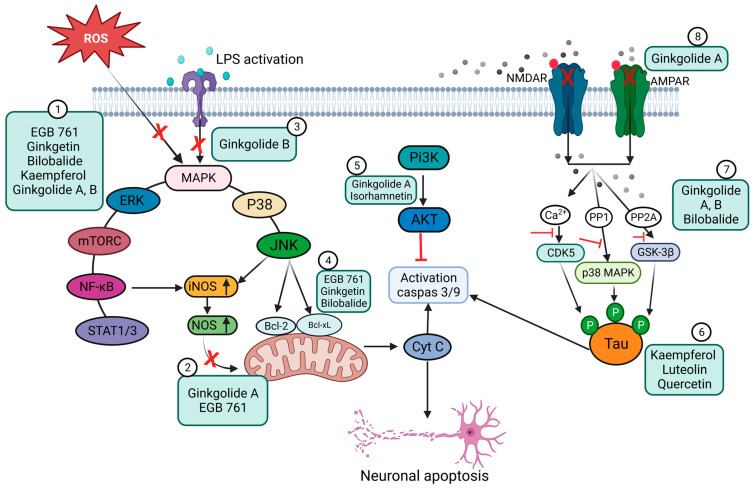
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb) and its constituents. (1) Inhibition of ROS and suppression of the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators (e.g., COX-2 and NO) and pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β) via the NF-κB signaling pathway. EGb can also inhibit the STAT 1/3 pathway. (2) Blocking of iNOS expression through a reduction in NO levels. (3) Inhibition of LPS-induced inflammatory response. (4) Prevention of mitochondrial oxidative stress by promoting the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins. (5) Inhibition of TLR4-NF-κB signaling through the PI3K/Akt pathway. (6) Prevention of the intracellular accumulation of p-Tau and cellular protection from Tau-hyperphosphorylation-related toxicity. (7) Blocking signaling pathways that involve CDK5, p38 MAPK, and GSK-3β. (8) Inhibition of NMDA and AMPA receptors, preventing the phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). (Created with BioRender).