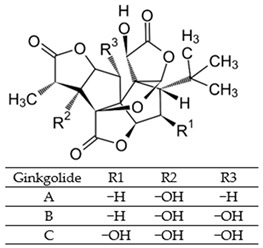
|
Leaves,
root, and
bark |
Anti-inflammatory actions by decreasing the expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, and NF-kB Antioxidant effects by inhibiting free radicals Anxiolytic-like effects Coffer neuroprotection by regulating pathways related to neurodegeneration and inflammation Anti-thrombotic action in inhibiting platelet aggregation by MMP-9 Controlling cAMP, thereby inhibiting intracellular Ca2+ mobilization and decreasing TXA2 activity Inhibited activation factor of platelets and signaling pathways, such as NIK/IKK α/I-kβ/NF-κB Activation of the p42/p44 (ERK) MAPK pathways, effect on mRNA levels and the protein from HIF-1α
|
[120,121,122,123,124,125,126] |
Bilobalide
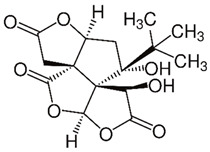
|
Leaves and
bark |
Decreased TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 levels Neuroprotection by reducing neuroinflammation and preventing Aβ deposition in AD Antioxidant effects by decreasing ROS Modulation of Bax, c-myc, and p53 proteins Activated Nrf2 and CREB through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, thus inhibiting apoptotic damage of nerve cells
|
[119,127,128] |
Isorhamnetin
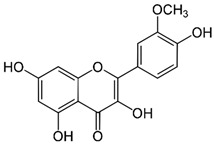
|
Leaves |
Improved brain function and cognition Anti-inflammatory/antioxidant properties Decreased apoptosis and DNA fragmentation Cleavage of PARP, impact on the ERK pathway and the activation of p53 protein Upregulation of genes related to Bcl-2 Downregulation of the BH3 gene and genes related to Bax
|
[117,129,130,131] |
Ginkgolic acid
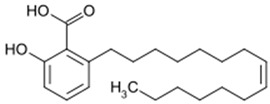
|
Leaves |
Neuroprotection against Aβ-induced impairment of neurotransmitter release and synaptic plasticity Antiviral and antibacterial effects by suppressing the fusion of enveloped viruses, including SARS-CoV-2 Promotion of autophagy-dependent clearance of α-syn aggregates
|
[132,133] |
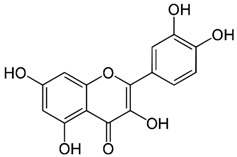
Quercetin
|
Leaves |
Upregulated BDNF levels Inhibited degradation of serotonin by monoamine oxidases Impact on the transcription of TNF-α Activation of ERK and JNK Decreased lipid peroxidation in the plasma and phosphorylation of I-kβ Upregulation of HMOX-1 Free-radical elimination
|
[129,134,135,136] |
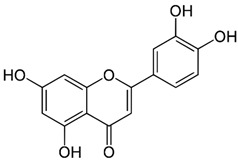
Luteolin
|
Leaves |
Anti-inflammatory effect by suppressing TNF-α, IL-6, COX-2, and NF-kB expression Antioxidant effect by scavenging ROS Neuroprotective action by inhibiting Aβ deposition and augmenting neuroinflammation in the brain
|
[137,138] |
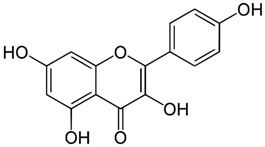
Kaempferol
|
Leaves |
Upregulation of GSH and suppression of oxidative and inflammatory damage to brain cells Inhibition of NF-kB, COX-2, and iNOS expression Protection against ischemia/reperfusion syndrome and myocardial injury Upregulation of BDNF, GCLC, and Bcl-2 levels Decrease in neurotoxicity induced via 3-NP, elevation of Bax, and upregulation of HMOX-1
|
[104,105,107] |







