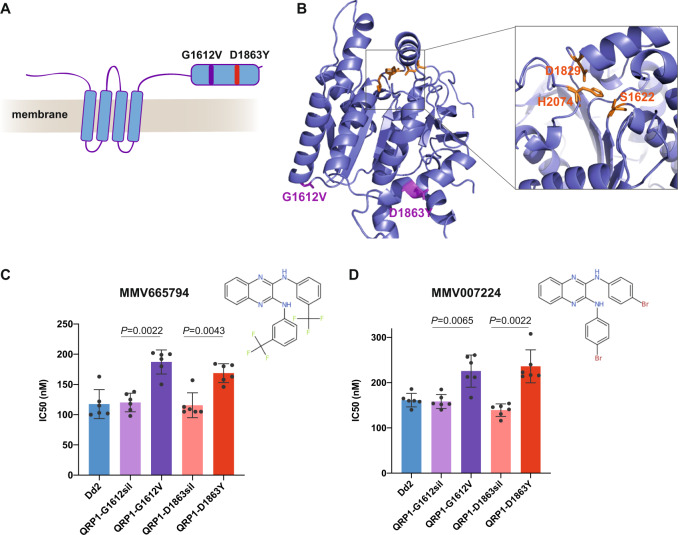
Fig. 5. QRP1 confers resistance to quinoxaline compounds.
A PfQRP1 (PF3D7_1359900) encodes a 250 kDa protein with four predicted transmembrane domains. The two mutations G1612V and D1863Y found in two independent selections with MMV665794 are located in a C-terminal domain that shares conservation with α/β hydrolases. B Model of the C-terminal 656 residues (1471–2126) of PfQRP1 showing the putative catalytic triad of Ser-Asp-His (yellow), and the G1612V and D1863Y resistance mutations (purple). C, D IC50 values of CRISPR-Cas9 edited QRP1. Dd2 lines encoding the equivalent G1612V and D1863Y mutations showed a significantly reduced susceptibility against MMV665794 and were cross-resistant to MMV007224, a structurally related molecule sharing the quinoxaline scaffold, in comparison with Dd2-WT and silent edited controls. Each dot represents a biological replicate, with n = 6 independent replicates with mean ± SD shown, and statistical significance relative to silent-edited controls determined by two-sided Mann–Whitney U test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.