Fig. 6.
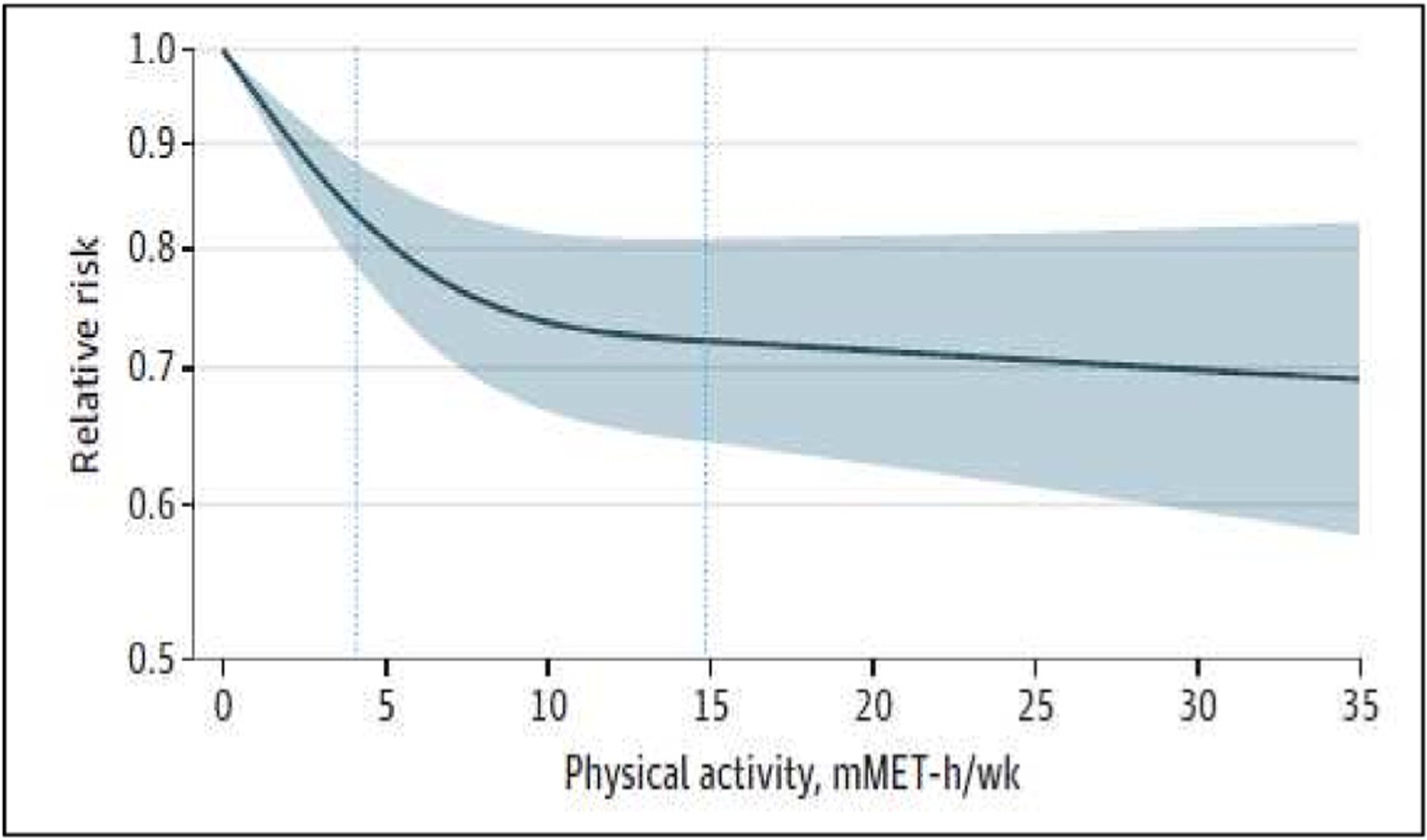
Association between physical activity level and risk for depression, from meta-analysis of 119,130 participants in 15 studies. An inverse curvilinear relationship between dose of physical activity and depression is noted, with the greatest reduction occurring at low levels of physical activity. (Reproduced with permission from Pearce et al.74).
