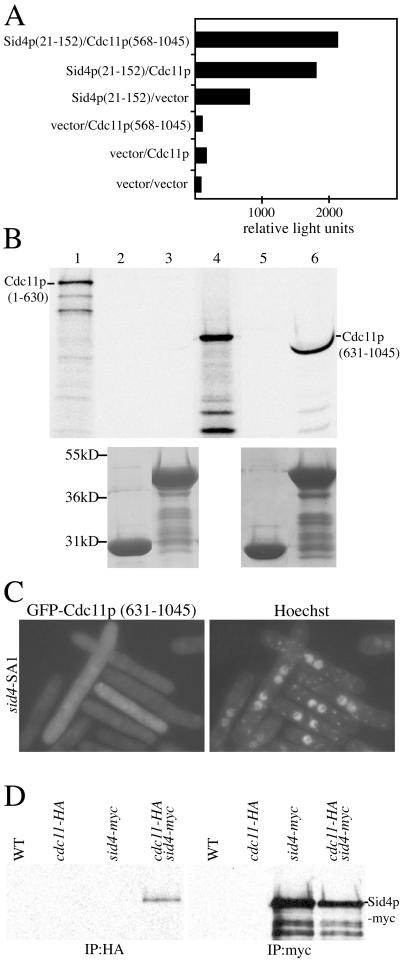
Figure 7.
Cdc11p binds Sid4p directly. (A) The Sid4p(21–152) bait plasmid was cotransformed with either Cdc11p full-length or Cdc11p(568–1045) prey plasmids into the S. cerevisiae strain PJ69–4A. Leu+Trp+ transformants were scored for β-galactosidase activity in relative light units. (B) GST-Sid4p(1–191) binds directly to Cdc11p(631–1045). Approximately equal amounts of GST (lanes 2 and 5) and GST-Sid4p(1–191) (lanes 3 and 6) bound to glutathione beads were mixed with in vitro translated Cdc11p(1–630) (lanes 2 and 3) or Cdc11p(631–1045) (lanes 5 and 6). After extensive washes, the proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and detected by autoradiography (upper panel) or Coomassie staining (lower panel). Lanes 1 and 4 represent samples of in vitro translated Cdc11p(1–630) and Cdc11p(631–1045), respectively, before the binding reaction. Lane 6 shows a compression due to GST-Sid4p(1–191) and Cdc11p(631–1045) having similar molecular weights. (C) Cdc11p SPB localization requires Sid4p. sid4-SA1 (KGY1234) cells expressing pREP41GFP Cdc11p(631–1045) were grown in the absence of thiamine to induce GFP-Cdc11p (631–1045) and then shifted to 36°C for 4 h to inactivate Sid4p. (D) Cdc11p-HA and Sid4p-myc interact in vivo. Lysates from wild-type (KGY246), cdc11-HA (KGY3202), sid4-myc (KGY1340), and the double-tag strain (KGY3713) were immunoprecipitated using anti-HA (12CA5) or anti-myc (9E10) antibodies. After SDS-PAGE, samples were blotted with anti-myc (9E10) antibodies.