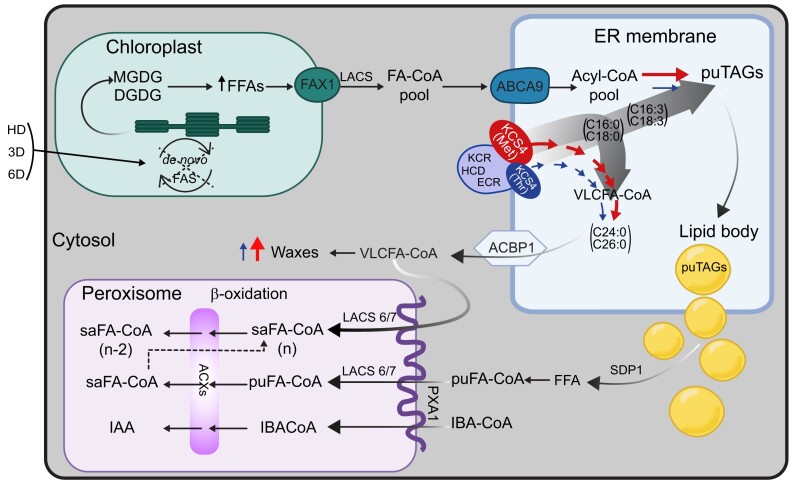
Figure 8.
Model summarizing the role of KCS4 on FA fate in Arabidopsis under carbon starvation. The lack of de novo FA synthesis under heat and darkness (HD) or extended darkness (3D, 6D) induces the degradation of galactolipids (MGDGs and DGDGs) from the chloroplasts’ thylakoids. FFAs are then exported to the ER (FA-CoA pool), where KCS4 is localized and acts as a branch point in the fate of FAs, channeling saturated FAs to VLCFA elongation and tipping the balance to a higher polyunsaturated-to-saturated-FA ratio for puTAG accumulation (degrade grey arrows). Two KCS4 alleles have differential capacity to allocate saturated FAs into the VLCFA pathway, with a major -more efficient- allele, KCS4(Met), and a minor -weaker allele, KCS4(Thr), exemplified here in different sizes. KCS4(Met) accessions efficiently channel the saturated FA from the Acyl-CoA pool to cuticular waxes, as they present higher accumulation of waxes than KCS4(Thr) accessions under stress. In addition, polyunsaturated TAG (puTAGs) levels are, therefore, higher in KCS4(Met) accessions compared to KCS4(Thr) accessions, as the result of a rise in the ratio of polyunsaturated-to-saturated FAs going to TAG formation. VLCFA-CoA produced by the elongase complex (here exemplified by KCS4, KCR, HCD, ECR) go to increase the cuticular waxes under HD and/or directly serve as a source of carbon undergoing degradation in the peroxisome; whereas puTAGs accumulate into lipid bodies first. FFAs are then released from lipid bodies by the action of lipases (SDP1) and further imported to the peroxisome to undergo β-oxidation. Acronyms: ABCA9 (ATP-BINDING CASSETTE A9; AT5G61730), ACBP-1 (Acyl-CoA-binding protein 1; AT5G53470); ACX (ACYL-COA OXIDASE); CoA (coenzyme A); DGDG (digalactosyldiacylglycerol); ECR (ENOYL-COA REDUCTASE; AT3G55360); FAs (fatty acids); FAS (fatty acid synthesis); FAX1 (FATTY ACID EXPORT1; AT3G57280); FFAs (free fatty acids); HCD (β-HYDROXYACYL-COA DEHYDRATASE); IAA (indol-3-acetic-acid), IBA (indol-3-butyric-acid), KCR (β-KETOACYL REDUCTASE); KCS4(Met/Thr) (3-KETOACYL-COA SYNTHASE4); LACS (LONG-CHAIN ACYL-COA SYNTHETASE); SDP1 (SUGAR DEPENDENT1; AT5G04040); MGDG (monogalactosyldiacylglycerol); PXA1 (PEROXISOMAL ABC-TRANSPORTER 1; AT4G39850); pu (polyunsaturated), sa (saturated), TAGs (triacylglycerols); VLCFA (very long chain fatty acid).