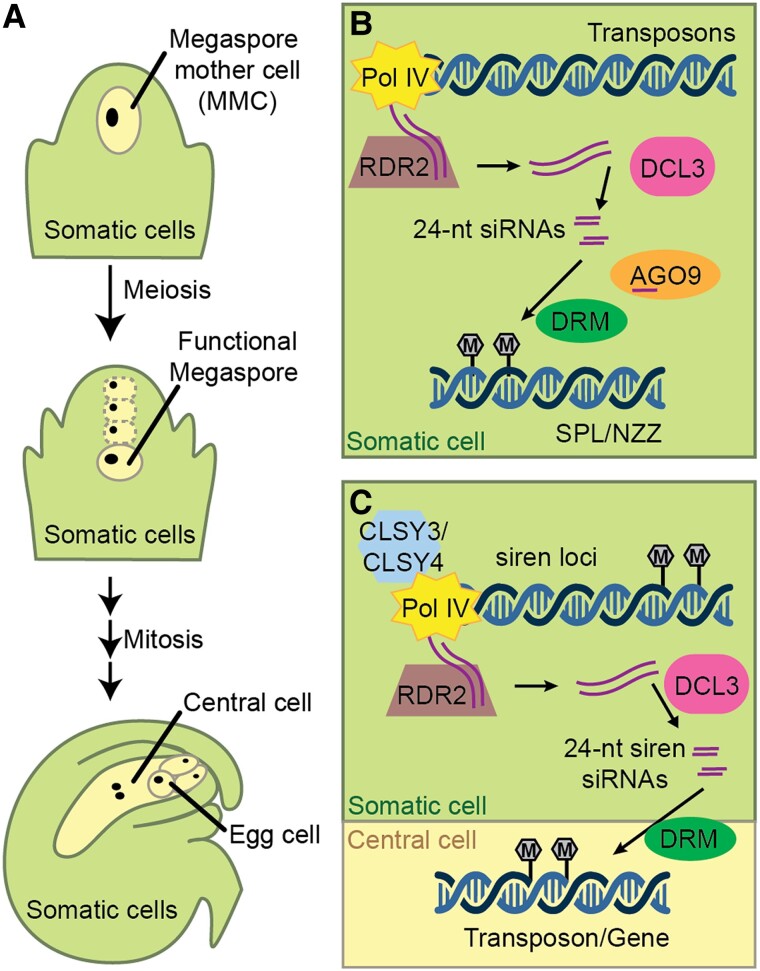
Figure 2.
Female reproductive development and the action of maternal 24-nt reproductive siRNAs. A, Female germ line development. Within each ovule, a single MMC undergoes meiosis to generate four haploid megaspores. Three of these degenerate, leaving a single functional megaspore. The megaspore goes through three rounds of nuclear division before cytokinesis to generate a 7-celled female gametophyte (antipodal cells not shown). The female gametophyte contains a binucleate central cell and a haploid egg cell that are ready for fertilization. The female germ line is surrounded by somatic cells throughout this development. B, Before meiosis, Pol IV, RDR2, and DCL3 produce 24-nt siRNAs, which interact with AGO9 to mediate DNA methylation and transcriptional gene silencing of SPL/NZZ via DRM1 and/or DRM2 (DRM). Regulation of SPL/NZZ is required for the specification of a single MMC. C, In somatic cells of a mature ovule, CLSY3 and CLSY4 direct Pol IV to transcribe siren loci. These transcripts are converted into double stranded by RDR2 and further processed into 24-nt siren siRNAs by DCL3. siren siRNAs induce methylation at protein coding genes in somatic cells and are proposed to move intercellularly, causing methylation in the gametophyte.