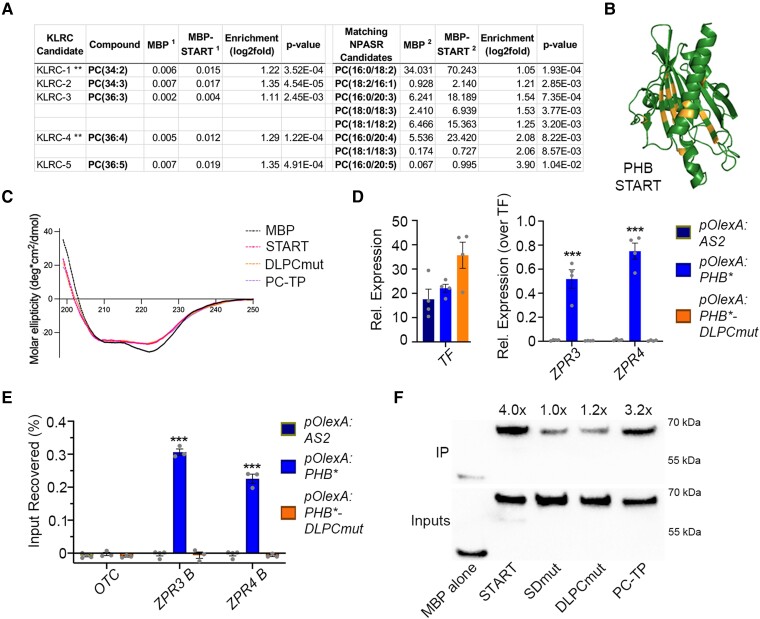
Figure 6.
PHB START domain binds PC and mutating predicted PC-contacting residues abolishes PC-binding and PHB DNA-binding competence. A) LC-MS analysis of lipids bound by recombinant MBP and MBP-START proteins after liposome incubation and repurification. Several species of PC are significantly enriched in MBP-START. Raw signal intensities are reported, ** indicates species preferentially bound by PC-TP (de Brouwer et al. 2001). B) Homology modeling of DLPCmut START variant showing position of mutations (orange). C) Circular dichroism of MBP, MBP-START, MBP-DLPCmut, and MBP-PC-TP showing all three recombinant START proteins have virtually identical secondary structures. D) Unlike PHB, PHB-DLPCmut cannot activate ZPR3 or ZPR4 targets in 24 h estradiol-induction experiments. E) PHB-DLPCmut does not bind ZPR3 or ZPR4 regulatory regions occupied by PHB. F) MBP fusions of PHB-START and PC-TP strongly bind to PC-conjugated beads, whereas binding of MBP-SDmut and MBP-DLPCmut is indistinguishable from that of the MBP negative control. IP enrichments were calculated by first normalizing each protein to its input then to the MBP alone IP/Input value. n = 3 or 4 biological replicates. ***P ≤ 0.001, Student's t-test.