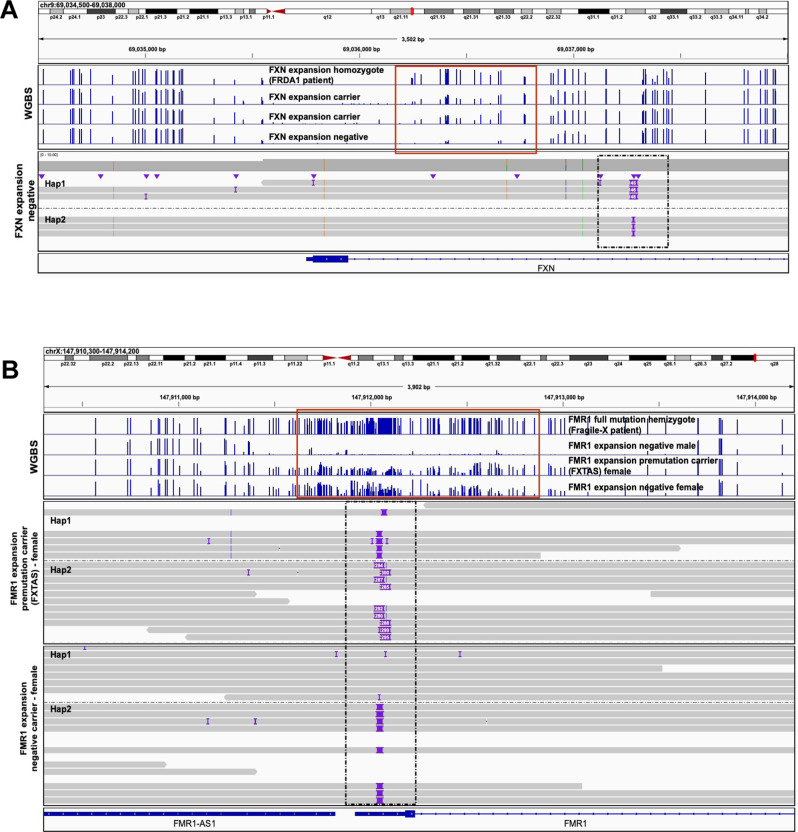
Fig. 1. Whole-genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS) and HiFi-genome sequencing (HiFi-GS) in patients with unstable repeat disorders.
A Genomic view of 2.7 kb on chromosome 9 at the FXN locus showing one individual homozygous for the FXN expansion at pathogenic range (>65 repeats) causing the autosomal recessive disorder Friedrich’s Ataxia (FRDA1), two FXN expansion carriers, and one individual without the expansion at a pathogenic range (<65 repeats, FXN expansion-negative). Blue tracks show the methylation level of CpGs measured by WGBS (y axis, 0–100%) with hypermethylation footprint (red box) linked to pathogenic repeat expansion (>65 repeats). Gray tracks show haplotype-resolved repeat expansion by HiFi-GS (black box, dashed line) in an individual without the expansion at a pathogenic range (<65 repeats, FXN expansion-negative). B Genomic view of 3.7 kb on X chromosome at the FMR1 locus showing an hemizygote individual with Fragile X (>200 repeats), one female FMR1 premutation carrier (55–200 repeats), and two individuals without the FMR1 expansion (male and female, <55 repeats). Blue tracks show the methylation level of CpGs measured by WGBS (y axis, 0–100%) with hypermethylation footprint (red box) linked to pathogenic repeat expansion (>200 repeats). Gray tracks show haplotype-resolved FMR1 repeat expansion (black box, dashed line) by HiFi-GS in one premutation carrier and one expansion-negative female. Hap1 denotes haplotype 1 and Hap2 denotes haplotype 2.