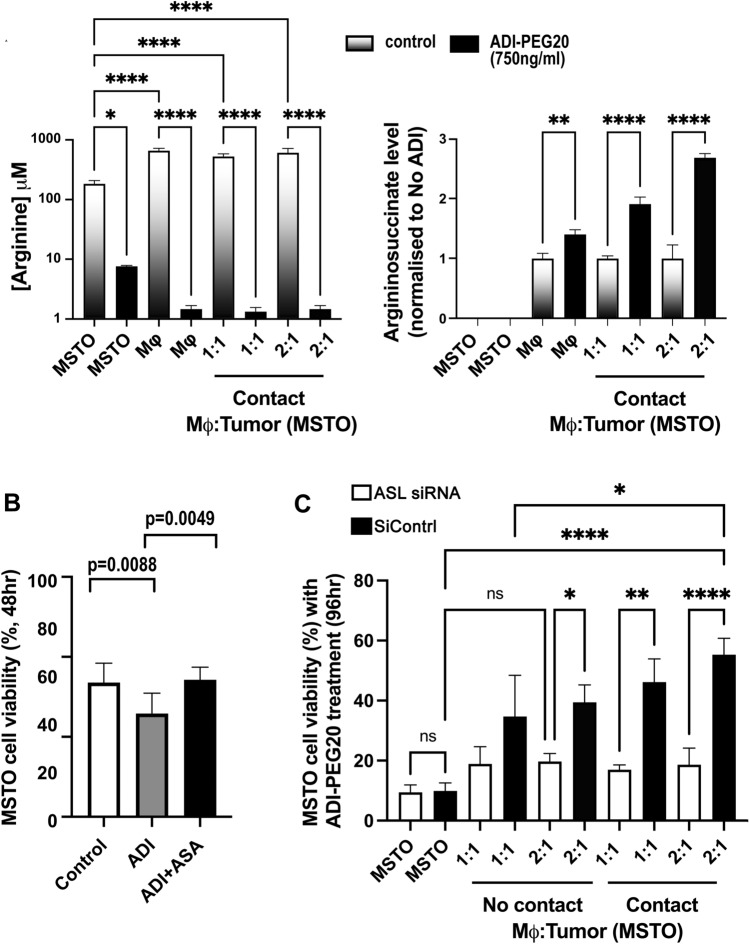
Fig. 4.
Macrophage-derived argininosuccinate bypasses ADI-PEG20 cytotoxicity in MPM cells. A Mean [arginine] and [argininosuccinate] in the supernatant from macrophage and MSTO tumor cells alone and co-cultured (with and without direct cell contact) by 48 h following ADI-PEG20 treatment using LC/MS (n = 3). Bars show mean and standard deviation: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001; two-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s test ([arginine], F7,14 = 92.90, df = 7; p < 0.0001), [argininosuccinate], (F7,14 = 213.3, df = 7; p < 0.0001); (B Argininosuccinate rescue (using 0.5 µg/ml, i.e., peak concentration measured above) with MSTO tumor cell viability assessed at 2 days in the presence of ADI-PEG20 (n = 6). Bars represent mean values and standard deviation: **p < 0.01; one-way ANOVA with uncorrected Fisher’s LSD post hoc test (F2,15 = 6.670, df = 2; p < 0.0085); and C the effect of ASL mRNA knockdown in the MSTO MPM cell line on the metabolic resistance conferred by macrophage-derived argininosuccinate. Cell viability was assessed at 4 days by flow cytometry. Bar values representing the mean and standard deviation (n = 3): *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001; two-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s test (F9,18 = 17.30, df = 9; p < 0.0001)