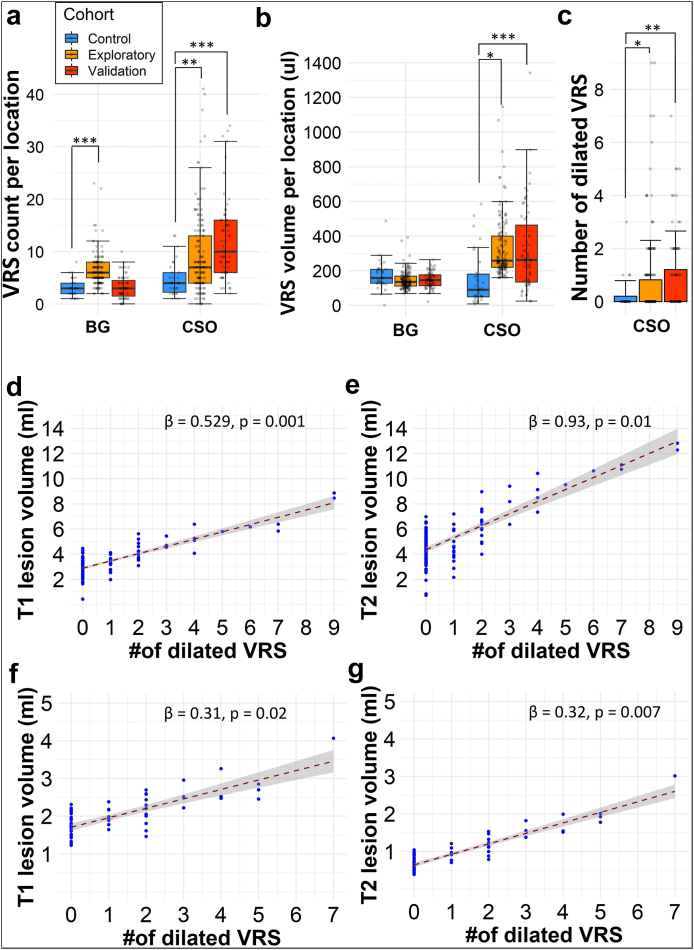
Fig. 2.
Dilated VRS are associated with higher T1 and T2 lesion volumes. Higher VRS counts (a), volumes (b), and number of dilated VRS (diameter ≥2 mm, (c)) in MS patients compared to controls (Exploratory cohort: n = 142; validation cohort: n = 63; control cohort: n = 30). The count of dilated perivascular spaces (VRS, diameter ≥ 2 mm) was associated with higher MRI T1 lesion (d) and T2 lesion volume (e) in our exploratory cohort (n = 142). These associations were substantiated in the validation cohort (n = 63, (f and g)). The corresponding slope of the regression line (β) and p values are displayed at the top right corner of each graph. The regression models are adjusted for patient age and sex. Asterisks indicate statistical significance between cohorts: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Abbreviations: BG, basal ganglia; CSO, centrum semiovale; VRS, Virchow-Robin space.