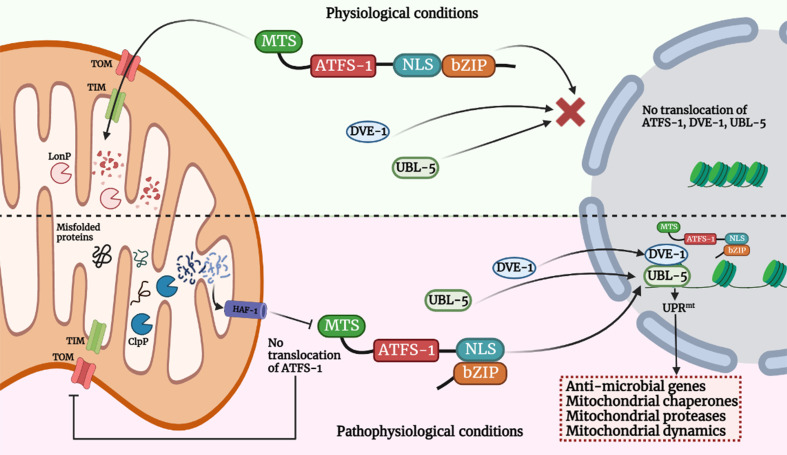
Figure 1.
Model for UPRmt signaling pathway. Activation of the UPRmt in cells occurs in response to different stress signals such as mtROS, mutation in mtDNA, accumulation of misfolded mitochondrial proteins in the mitochondrial matrix or in IMS and alteration in mitochondrial membrane potential due to bacterial infection. Such events trigger the translocation of ATFS-1 (mammal homologue - ATF-5) which is bZIP protein, and contains MTS and NLS sequence into the nucleus and along with DVE-1 and UBL-5, it induces a transcriptional up-regulation program known as UPRmt. Under physiological conditions, it is imported in the mitochondria via TOM/TIM machinery and digested in the mitochondrial matrix by mitochondrial protease LonP which prevents activation of UPRmt. Under pathophysiological or stressed conditions, import of ATFS-1 is blocked in mitochondria. The misfolded proteins digested in the mitochondrial matrix via ClpP and efflux of such peptides into the cytoplasm via HAF-1 prevents ATFS-1 translocation into mitochondria, and therefore it moves into the nucleus and induces multiple genes which functions in restoring mitochondrial functions, innate immunity facilitating bacterial clearance. The image was created with the help of BioRender.com.