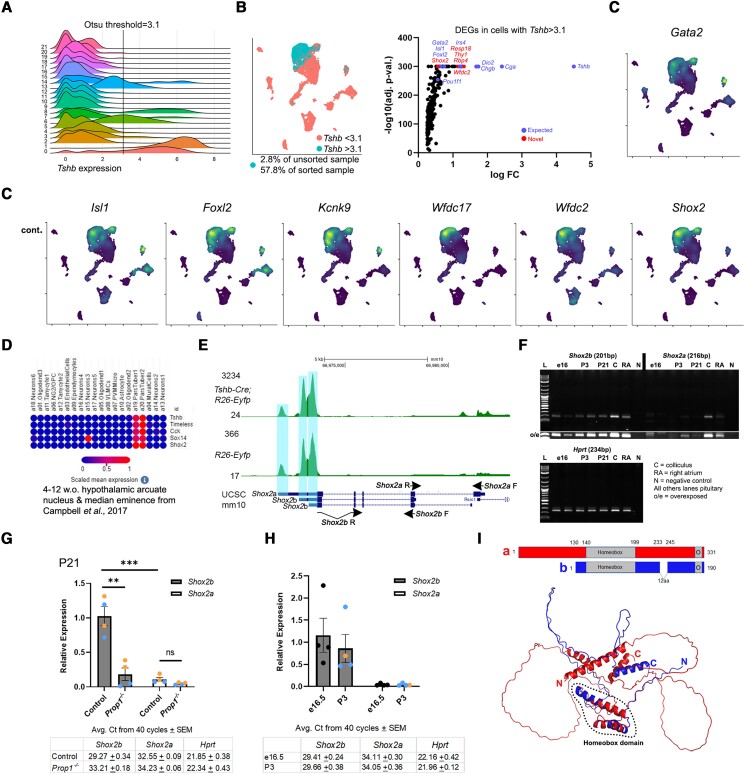
Figure 3.
Identification of Shox2b expression in thyrotropes. A, The Otsu method was used to determine a threshold for high Tshb expression and is shown on a ridge plot of Tshb expression distribution across Seurat-calculated clusters. Some clusters are clearly Tshb-high or -low. B, Cells in our data set were separated into two groups based on high or low Tshb expression (above/below Otsu's threshold) and differential expression analysis was performed. Known thyrotrope markers were found such as Isl1 and Foxl2. Novel expression associated with high Tshb expression included the transcription factor Shox2. D, Broad Single Cell Portal data set (SCP97) of adult hypothalamus arcuate nucleus also observed Shox2 enrichment in (pars tuberalis) thyrotropes (48). E, Sequence alignment map of reads from the sorted and unsorted samples show appropriate peaks at the ends of Shox2 transcript variants and no overlapping genes that could cause alignment issues. F, Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) using Shox2a- and Shox2b-specific primers shows consistent expression of the Shox2b isoform in pituitary tissue from embryonic and early postnatal ages. No stringent band is observed for Shox2a even when the image was overexposed. G, qPCR of Prop1-mutant mice showed large reduction in Shox2b. H, qPCR of controls showed Shox2b expression is relatively similar from development to early postnatal and Shox2a is virtually undetected. I, Shox2a and Shox2b predicted protein structures both retain the homeobox and otp, aristaless, and rax (OAR; O) domains with no other domains identified (Alphafold).