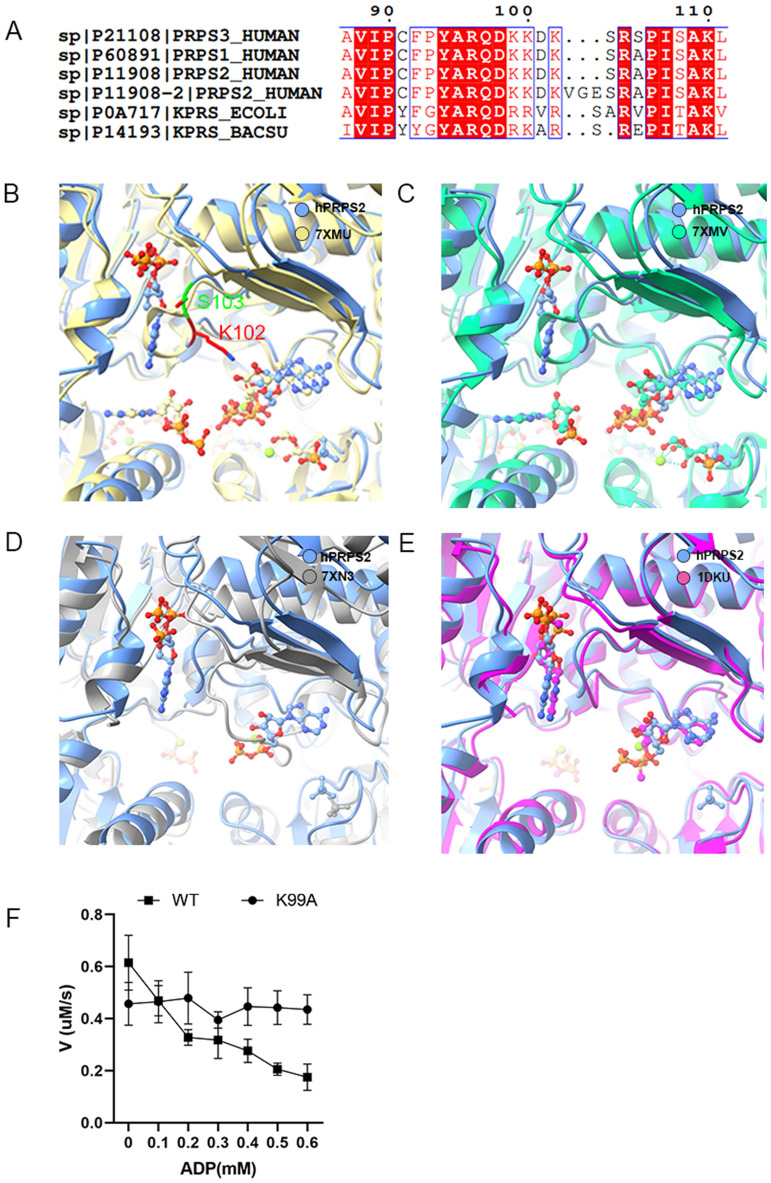
Fig. 6.
Comparison of PRPS ligands in different organisms. A The sequence alignment of RF loop of hPRPS1-3, E. coli PRPS and Bacillus subtilis PRPS. Structural comparison between human PRPS2 with E. coli PRPS in type A filament (B: 7XMU), E. coli PRPS in type AADP+AMP filament (C: 7XMV), E. coli PRPS in type B filament (D: 7XN3), and Bacillus subtilis PRPS (E: 1DKU). In (B) and (C), ADP in allosteric site 1 clashes with the RF loop in E. coli PRPS. The difference of the RF loop in hPRPS2 short isoform is indicated (K102 and S103) in (B). In (D), ADP binds to the ATP active site of hPRPS2. Unlike E. coli type B filament, RF loop of hPRPS2 does not occupy the ATP site. In (E), the RF loop of human PRPS2 is slightly different from that of Bacillus subtilis PRPS. (F) The results of ADP inhibition on hPRPS2-shortwt and hPRPS2-shortk99A. The activity of hPRPS2-shortk99A is low, but not inhibited by ADP