Figure 1.
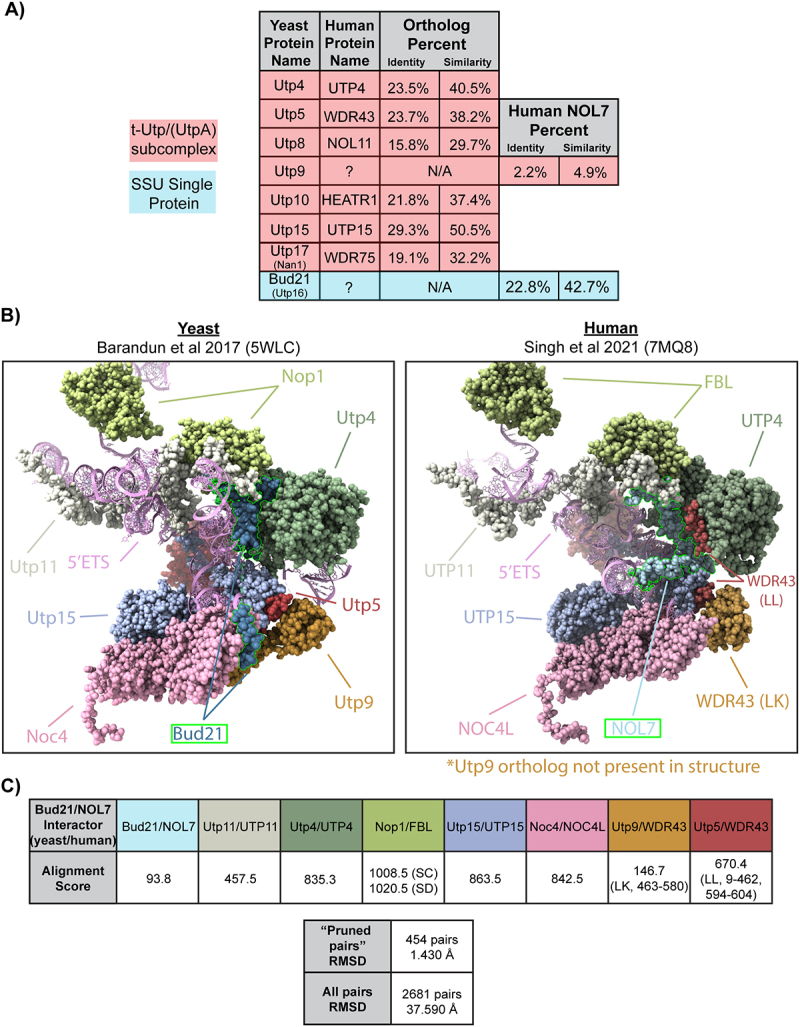
NOL7 is the likely Bud21 (Utp16) ortholog.
A. Human NOL7 contains the highest sequence similarity to yeast Bud21 (Utp16). Table of yeast and human t-UTP/UTPA subcomplex proteins and their orthologs including the yeast t-Utp interacting protein Bud21. Pairwise sequence alignments were performed using EMBOSS Needle2. Percent similarity and identity of NOL7 with two yeast Utp members that do not currently have a known human ortholog and established orthologous protein pairs are indicated.
B. Side-by-side structure comparison of Bud21 (Utp16) and NOL7 with their interaction partners in the small subunit processome. (Left) S. cerevisiae4 (pdb: 5WLC) and (Right) humans5 (pdb: 7MQ8). UCSD ChimeraX software was used to visualize Bud21 and NOL7 interacting proteins (space filling) and 5’-external transcribed spacer (5’ETS). Orthologous proteins are shown in same colouring and labelled. Bud21 and NOL7 are outlined in green. Utp9 is only present in the yeast structure, but WDR43 (chain LK) takes a similar position in the human structure.
C. Alignment score for Bud21 (Utp16) and NOL7 and their associated interacting proteins in the small subunit processome (SSU) to show similarities between analogous proteins from yeast to humans. Alignment scores for the indicated proteins were calculated based on BLOSUM-62 matrix scoring and secondary structure assignments. Scores for proteins with multiple chains are indicated by their abbreviations. Root-mean square deviation (RMSD) is reported for both ‘prune pairs’ and the entire yeast vs. human structures of proteins that interact with Bud21 and NOL7 in angstroms (Å).
