FIGURE 5.
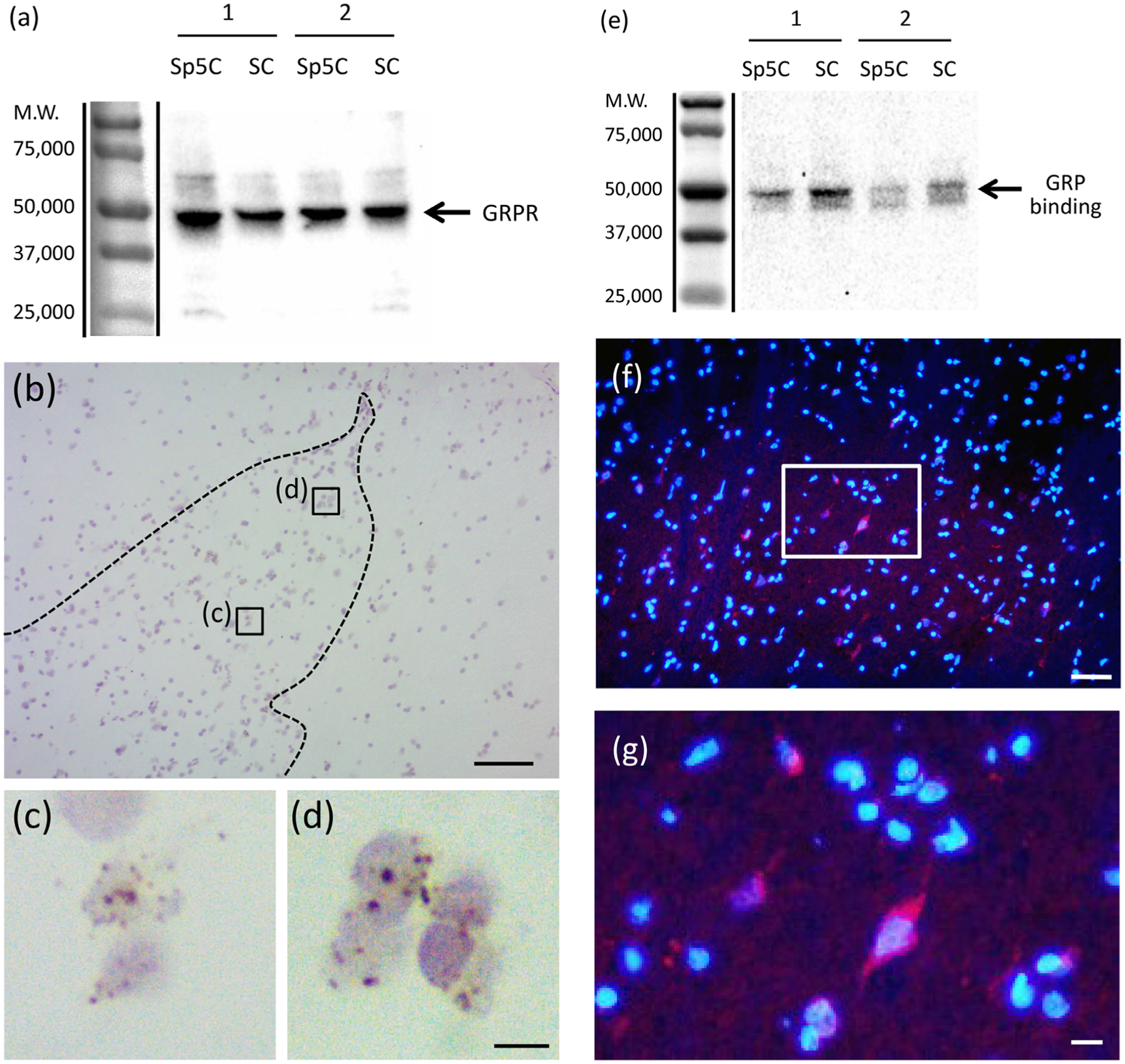
Expression of GRPR mRNA and GRPR protein and GRP binding sites in the sensory system of the adult macaque monkeys, (a) Expression of GRPR protein in the trigeminal and spinal cord. The number on the left indicates the molecular weight. The GRPR antiserum recognized a band at the expected molecular weight of GRPR (~43 kDa) on western blots of Sp5C and the dorsal horn of the cervical spinal cord (SC) of the macaque monkeys. Numbers 1,2 indicate different individuals. M.W. Molecular weight, (b–d) Localization of GRPR mRNA in the cervical spinal dorsal horn of the adult macaque monkey. GRPR mRNA was expressed in neurons within some superficial layers of the spinal dorsal horn (b–d). The reddish-brown dot structures were GRPR mRNA signals (c, d) and the nuclei were visualized in a light purple color by counterstaining with hematoxylin, respectively, (c and d) are enlargements of the boxed areas in (b), respectively. Bars = 100 μm (b); 10 μm (d). (e) Expression of the GRP-ligand binding sites in the trigeminal and spinal cord of the adult macaque monkeys. The number on the left indicates the molecular weight. The FITC-GRP-10 binding was recognized as an intense band at the expected molecular weight of GRPR (~43 kDa) on Western ligand blot of Sp5C and the dorsal horn of the cervical spinal cord (SC). Numbers 1,2 indicate different individuals. M.W. Molecular weight, (f, g) Ligand derivative staining with rhodamine-GRP-10 in the spinal cord of adult female macaque monkeys. Double staining of rhodamine-GRP-10 (red) and DAPI (blue). Rhodamine-GRP-10 signals were observed in a few neurons of the superficial layers of the cervical spinal dorsal horn, (g) is enlargements of the boxed area in (f). Bars = 50 μm (f); 10 μm (g)
