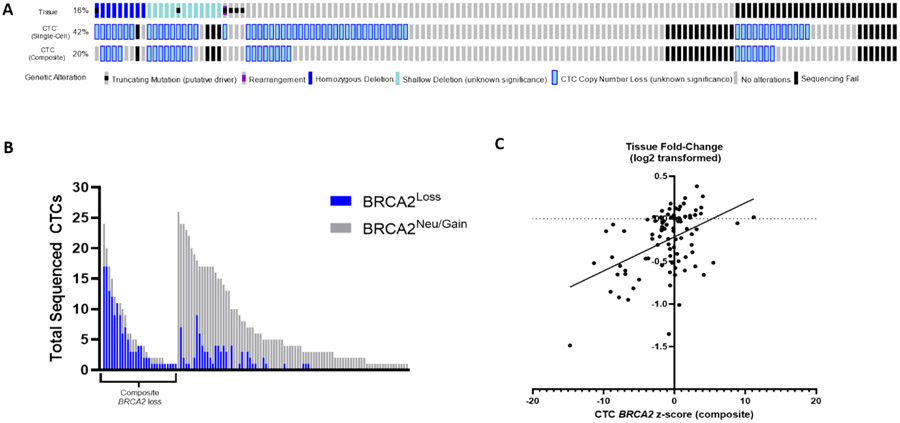
Fig. 4 –
Comparison of BRCA2 detection in tissue and CTCs. (A) Oncoprint of BRCA2 alterations detected by MSK-IMPACT tumor testing (top), single-cell CTC calling (middle, ≥1 CTC threshold), and composite CTC calling (bottom). Shallow deletions and CTC losses have unknown clinical significance. (B) Number of successfully sequenced CTCs, by BRCA2 status (blue, loss; gray, neutral). Each bar represents an individual patient (left, patients with any composite BRCA2 loss; right, patients without composite BRCA2 loss in CTCs; n= 115). (C) Linear regression model demonstrating a significant association between BRCA2 fold-change (log2 transformed) in tissue and composite CTC z score (91 matched sample pairs plotted). CTC = circulating tumor cell; MSK-IMPACT = Memorial Sloan Kettering-Integrated Mutation Profiling of Actionable Cancer Targets.