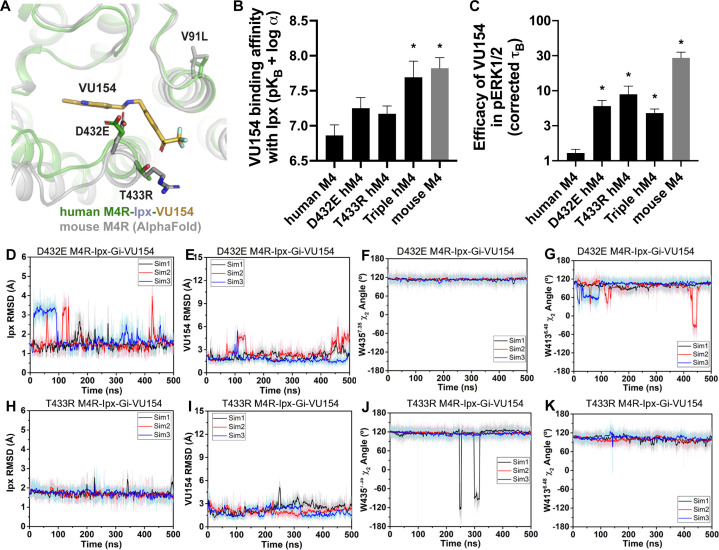
Figure 7. A molecular mechanism for the species selectivity for VU154.
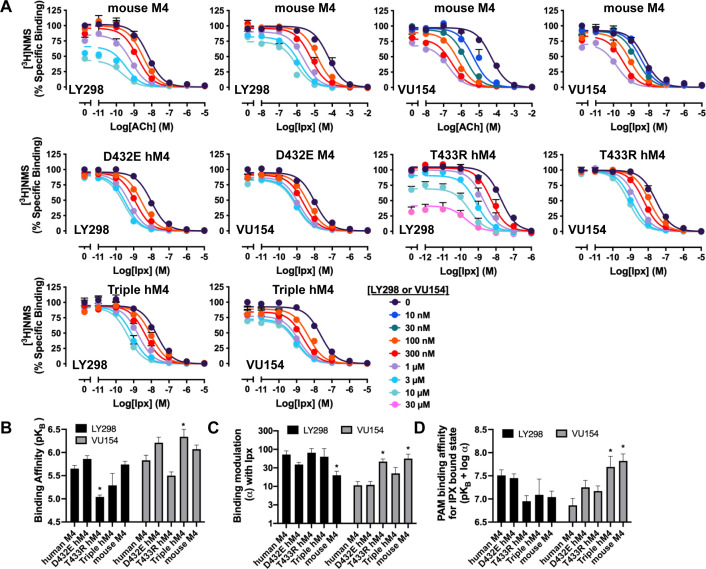
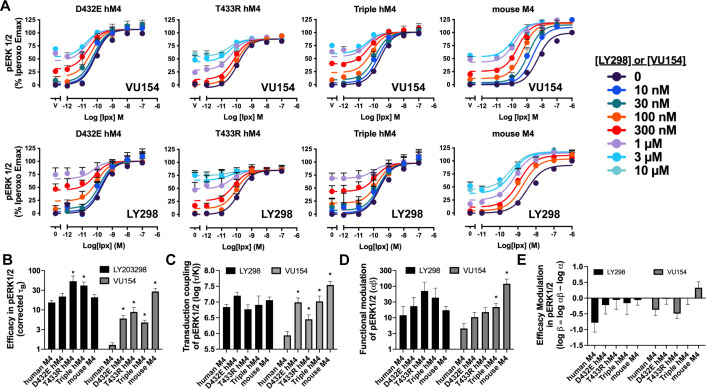
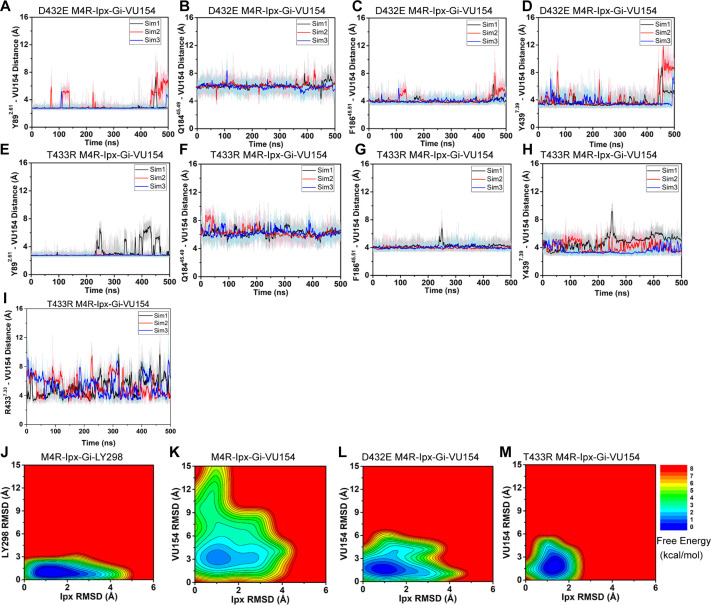
(A) Comparison of the cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the human M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) bound to Ipx-VU154 with the AlphaFold model of the mouse M4 mAChR (Jumper et al., 2021; Varadi et al., 2022). The three residues that differ between species and within the core 7TM bundle from the human receptor (V91, D432, and T433) are shown as sticks along with the corresponding residues from the mouse receptor. (B) The binding affinity of VU154 for the Ipx-bound conformation (pKB-Ipx = pKB + α) determined from [3H]-NMS binding experiments. Values calculated with data from Figure 7—figure supplement 1 with propagated error. (C) Efficacy of VU154 (τB – corrected for receptor expression) of pERK1/2 signaling from data in Figure 7—figure supplement 2. (D–K) Time courses of obtained from Gaussian accelerated molecular dynamics (GaMD) simulations of the (D–G) D432E and (H–K) T433R mutant M4R-Ipx-Gi1-VU154 systems with (D, H) Ipx RMSDs, (E, I), VU154 root mean square deviations (RMSDs), (F, J) W4357.35 χ2 angle, and (G, K) W4136.48 χ2 angle. Data shown are mean ± SEM from three or more experiments performed in duplicate with the pharmacological parameters determined from a global fit of the data. *Indicates statistical significance (p<0.05) relative to WT as determined by a one-way ANOVA with a Dunnett’s post-hoc test.