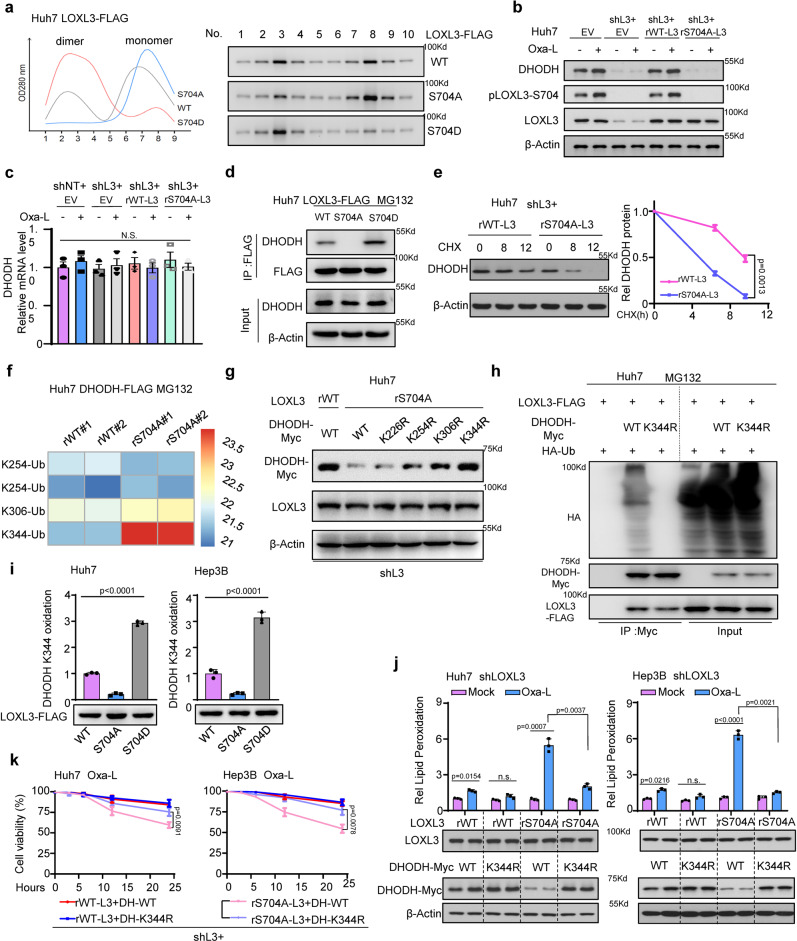
Fig. 3. LOXL3-S704 phosphorylation prevents DHODH-K344 ubiquitination and promotes DHODH stability to resist chemotherapy-induced ferroptosis.
a Huh7 cells stably expressing WT- or S704A-, S704D-mutant LOXL3-FLAG were enriched for R-FPLC analysis. b, c Indicated Huh7 cells with restored expression of WT- or S704A-mutant LOXL3 were treated with Oxa-L for WB (b) or qRT-PCR(c). d Huh7 cells expressing WT-, S704A- or S704D-mutant LOXL3-FLAG were treated with MG132 for 12 h and collected for Co-IP. e Huh7 shL3 cells expressing WT- or S704A-mutant LOXL3 were treated with CHX (2 μM) for the indicated time points and collected for WB (e, left). The protein decay was analyzed (e, right). CHX: cycloheximide. f, g Huh7 shL3 cells expressing WT or S704A mutant LOXL3 were transfected with DHODH-FLAG or DHODH-myc, including WT and mutants with the above lysine (K) sites mutated to arginine (R). Then, WT-DHODH was enriched and subjected to identify ubiquitin modifications by LC/MS analysis after cells were treated with MG132 for 12 h (f). The WT and KR mutants DHODH-myc protein level was detected by WB (g). h Huh7 cells expressing WT- or S704D-LOXL3 were transfected with DHODH-myc and HA-ubiquitin for 36 h and treated with MG132 for 12 h. An IP assay was performed and WB was carried out using the indicated antibodies. i Huh7 or Hep3B cells expressing WT- or S704A-, S704D-mutant LOXL3-FLAG were collected to enrich LOXL3-FLAG, which was incubated with peptide “ALEK344IRAGAS” as LOXL3 substrate. j Huh7 or Hep3B shL3 cells expressing WT- or S704A-mutant LOXL3 were transfected with WT- or K344R-mutant DHODH-FLAG for 48 h, and then lipid peroxidation levels and WB were assessed. k Huh7 or Hep3B shL3 cells expressing restored WT- or S704A-mutant LOXL3 with WT or K344R-mutant DHODH were treated with Oxa-L for the indicated time points, and cell viability was assessed. L3, LOXL3; DH, DHODH. For (c, e, i, k), data present means ± SEM from three independent experiments (n = 3) and the statistical analysis was calculated by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD post hoc test (c, i, j) or two-way ANOVA for multiple comparisons (e, k). Source data are provided as a Source Data file. See also Supplementary Fig. 3.