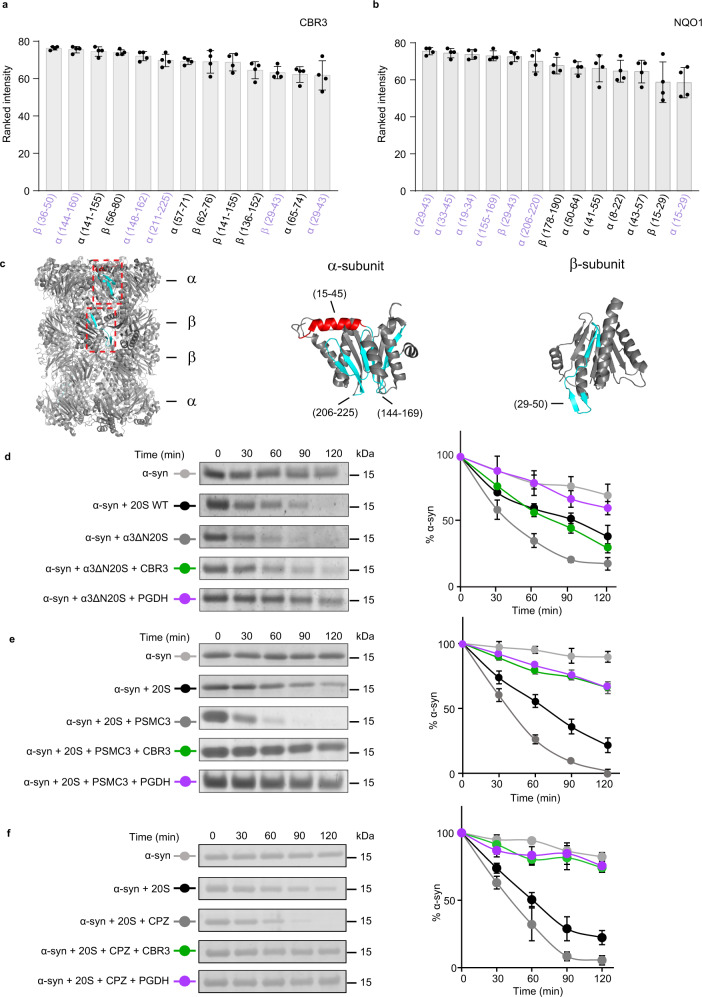
Fig. 6. CCRs do not bind to the 20S proteasome orifice.
a, b Peptide-array screening for CCR binding region to archaeal 20S proteasome derived peptides. The bar graphs present the average of the ranked intensities from four independent experiments for the relative binding of a CBR3 and b NQO1 to the various 20S proteasome peptides. Regions that are bound to both CBR3 and NQO1 are highlighted in lilac. Error bars represent SD. c 20S proteasome peptide sequences bound to both CBR3 and NQO1 are highlighted in red for α-helices and in cyan for β-strands, on α- and β-subunits of the 20S proteasome structure. d Representative in vitro degradation assays using the yeast open-gate mutant (α3ΔN) and the wild-type (WT) 20S proteasome. Assays were performed with the model substrate α−synuclein (α-syn) and the mammalian CCRs CBR3 and PGDH. e, f In vitro degradation assays using the rat 20S proteasome and α-syn, in the presence of CBR3 and PGDH with the gate opening peptide from the C-terminus of PSMC3 (e) and chlorpromazine (f). Averaged quantification of three independent experiments is displayed on the right. Error bars represent SD. Source data are provided with this paper.