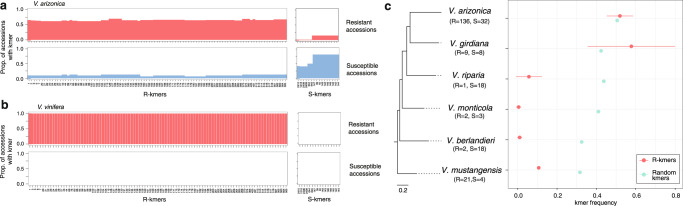
Fig. 4. The presence of resistance and susceptibility kmers in different data sets.
a Analyses within the V. arizonica sample set. The top-left graph indicates the 99 different resistance (R-kmers) kmers across the x-axis, with their detection frequency across the resistant (CFU/mL < 13) accessions. The top-right graph plots the average detection frequency of susceptibility kmers (S-kmers). The bottom-left and bottom-right graph are similar, they but show R-kmer and S-kmer detection frequencies among susceptible accessions. b The same graphs as in A, but the top graphs plot R-kmer and S-kmer detection frequencies for the five V. vinifera cultivars bred for PD resistance by backcrossing to V arizonica, while the bottom graphs represent susceptible V. vinifera cutlivars. c. Plots of kmer frequencies in six Vitis species. The species phylogeny is shown on the left, with the average detection frequency of R-kmers shown in red dot. The gray dots represent average detection frequencies of randomly chosen kmers that had similar population frequencies in V. arizonica as the set of R kmers. Whiskers denote 95% confidence intervals.