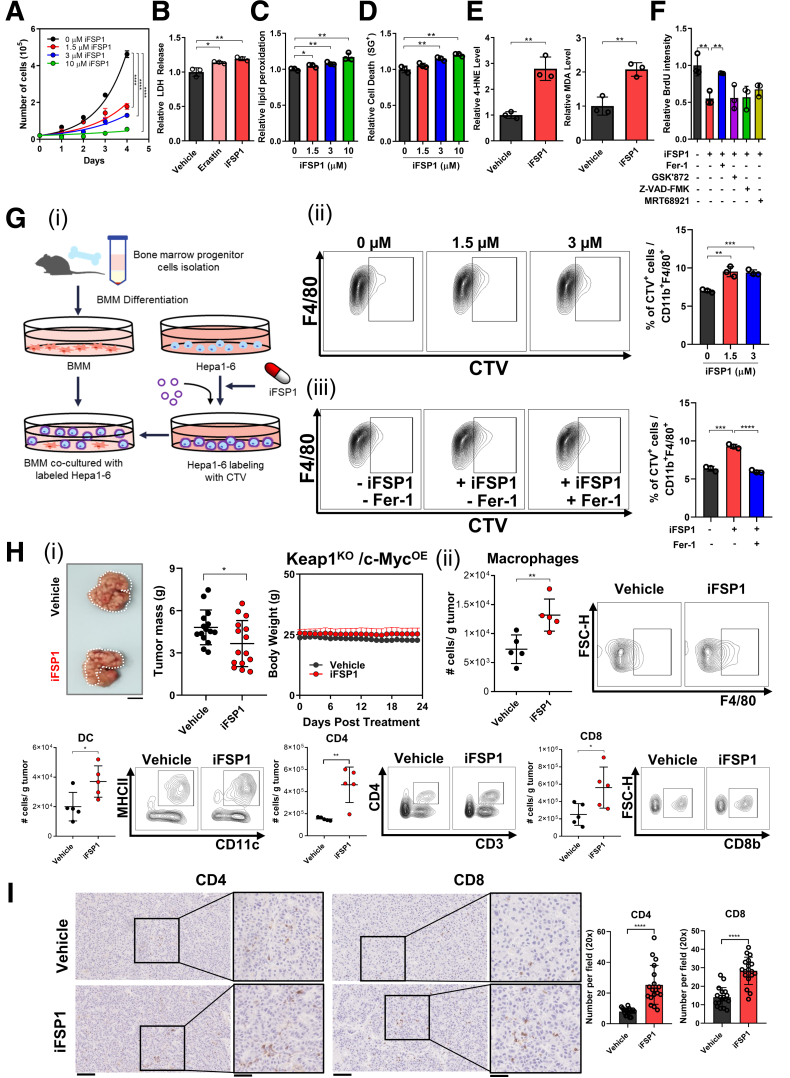
Figure 5.
iFSP1 induced ferroptosis and enhanced anti-tumor immune response. (A) Cell proliferation rates of MHCC97L cells determined by cell counting daily were significantly suppressed by treatments of 1.5, 3, and 10 μM FSP1 inhibitor iFSP1 in dose-dependent manner. (B) Quantification of relative LDH release from MHCC97L cells demonstrated that erastin and iFSP1 significantly induced cell death. (C) BODIPY 581/591 C11 staining in MHCC97L cells revealed significant increase of lipid peroxidation from treatments of 1.5, 3, and 10 μM iFSP1 in dose-dependent manner. (D) SYTOX Green (SG+) staining in MHCC97L cells revealed that treatments of 1.5, 3, and 10 μM iFSP1 resulted in significant increase in cell death dose-dependently. (E) Quantitative measurements of Left: 4-HNE and Right: MDA in MHCC97L cells with iFSP1 or vehicle treatment further suggested iFSP1 significantly increased lipid peroxidation. (F) Cell proliferation rates of MHCC97L cells treated with iFSP1 and vehicle determined using BrdU assay indicated that Fer-1, not inhibitors of other modes of RCD GSK’872 (necroptosis), Z-VAD-FMK (apoptosis), and MRT68921 (autophagy), can rescue proliferation rates suppressed by iFSP1 treatment. (G) Extent of phagocytosis by BMMs of iFSP1 pre-treated Hepa1-6 cells was determined by phagocytosis assay. (i) Schematic representation of the experimental design. (ii) Ferroptotic Hepa1-6 cells induced by iFSP1 pre-treatment were more frequently phagocytosed by BMMs. (iii) Fer-1 treatment abrogated the increase of phagocytosis by BMMs of iFSP1 pre-treated Hepa1-6 cells. (H) In vivo HCC tumors were induced via HDTVi of plasmids carrying Keap1KO/c-MycOE in C57BL/6N mice fed with HFD. (i) Administration of iFSP1 through intraperitoneal injection significantly reduced HCC tumor size compared with vehicle (n = 15 mice per experimental group). Left: Representative picture of harvested tumors. Middle & Right: Quantifications of tumor mass and body weight of mice. (ii) Administration of iFSP1 enhanced infiltration of macrophages, DCs, CD4+ T cells, and CD8+ T cells in HDTVi-induced HCC tumors. (I) IHC staining demonstrated the administration of iFSP1 enhanced the recruitment of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in HDTVi-induced HCC tumors. Left: Representative staining of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from harvested tumors treated with Vehicle or iFSP1. Right: Quantifications of number of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells stained per field. Error bars indicate mean ± SD. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001, ∗∗∗∗P < .0001 vs vehicle or 0 μM as indicated. Student’s t test. H: Scale bar = 1 cm. I: original = 20× magnification, scale bar = 100 μm; Inset = 40× magnification, scale bar = 50 μm