Figure 2.
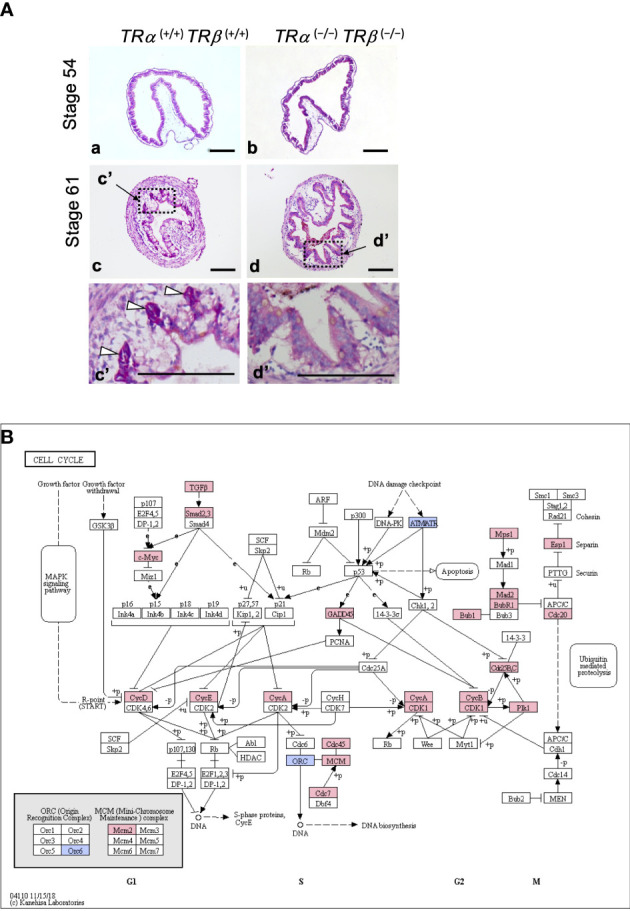
(A) TR double knockout tadpoles have abnormal intestinal morphology with premature adult type epithelial folding. Cross-sections of the intestine of indicated genotypes stages were stained with methyl green-pyronin Y. (a, c): Wild type TRα (+/+)TRβ (+/+) ; and (b, d): TR double knockout TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−) . Dashed boxes in c and d are shown in higher magnification in c’ and d’, respectively. White arrowheads point to the clusters of proliferating adult epithelial stem cells adjacent to/underneath the degenerating larval epithelium (vacuole-like, poorly stained) at the climax of metamorphosis (stage 61) in wild type tadpoles. Note that the knockout tadpoles lacked such clusters at stage 61 and the epithelium appeared to be uniform without any obvious degeneration, but with numerous folds. Bars: 100 μm. See (73) for details. (B) TRα is required for the activation of many cell cycle genes during early phase of T3-induced intestinal remodeling. Genes regulated by at least 2.0-fold after 18 hours of T3 treatment in stage 54 wild type but not TRα knockout tadpoles were mapped onto the KEGG pathway for cell cycle. Pink boxes indicate upregulation and blue boxes indicate downregulation. Note that most of the regulated genes were upregulated by T3. See (72) for more details.
