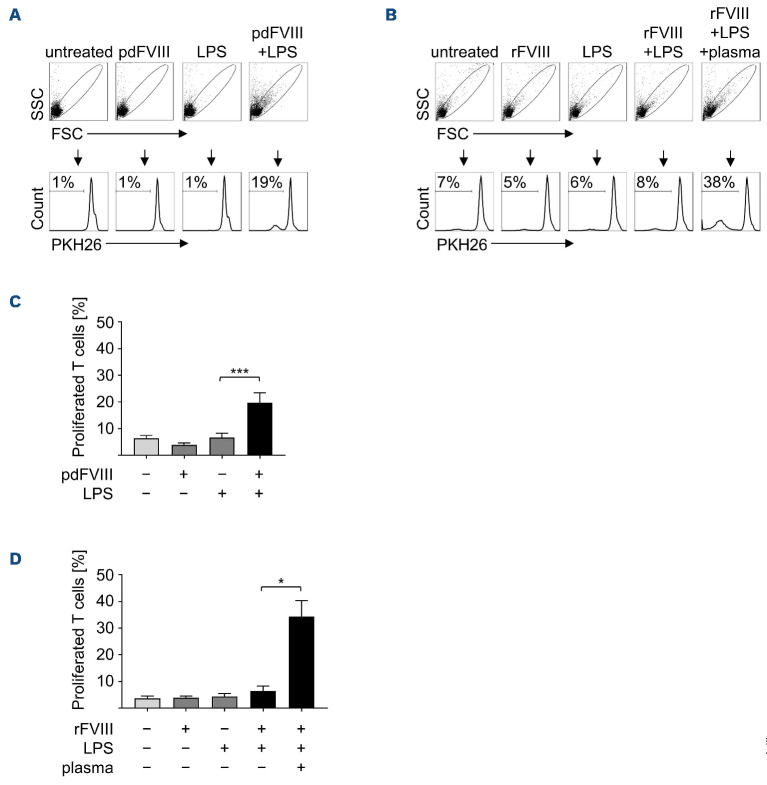
Figure 1.
Addition of human plasma to recombinant FVIII plus lipopolysaccharide-treated dendritic cells induces increased T-cell proliferation. Dendritic cells (DC) were treated for 24 hours with (A) plasma-derived (pd) FVIII or (B) rFVIII (each with 1 IU/mL), lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (0.1 mg/mL), or with FVIII plus LPS. In addition, DC were treated with rFVIII plus LPS in presence of plasma (2.5 mL/mL). Untreated DC served as control. PKH26-labeled autologous T cells were added and at day 9 of co-culture, cells were harvested and percentages of proliferated T cells were analyzed by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). Flow cytometry plots of 1 representative donor are shown in (A) and (B). Data of several donors are summarized from at least 3 independent experiments for (C) pdFVIII (n=14) and (D) rFVIII treatment (n=7-10). Statistical significance was determined using the Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. Error bars indicate the means ± standard error of the mean. *P<0.05; ***P<0.001.