Figure 5.
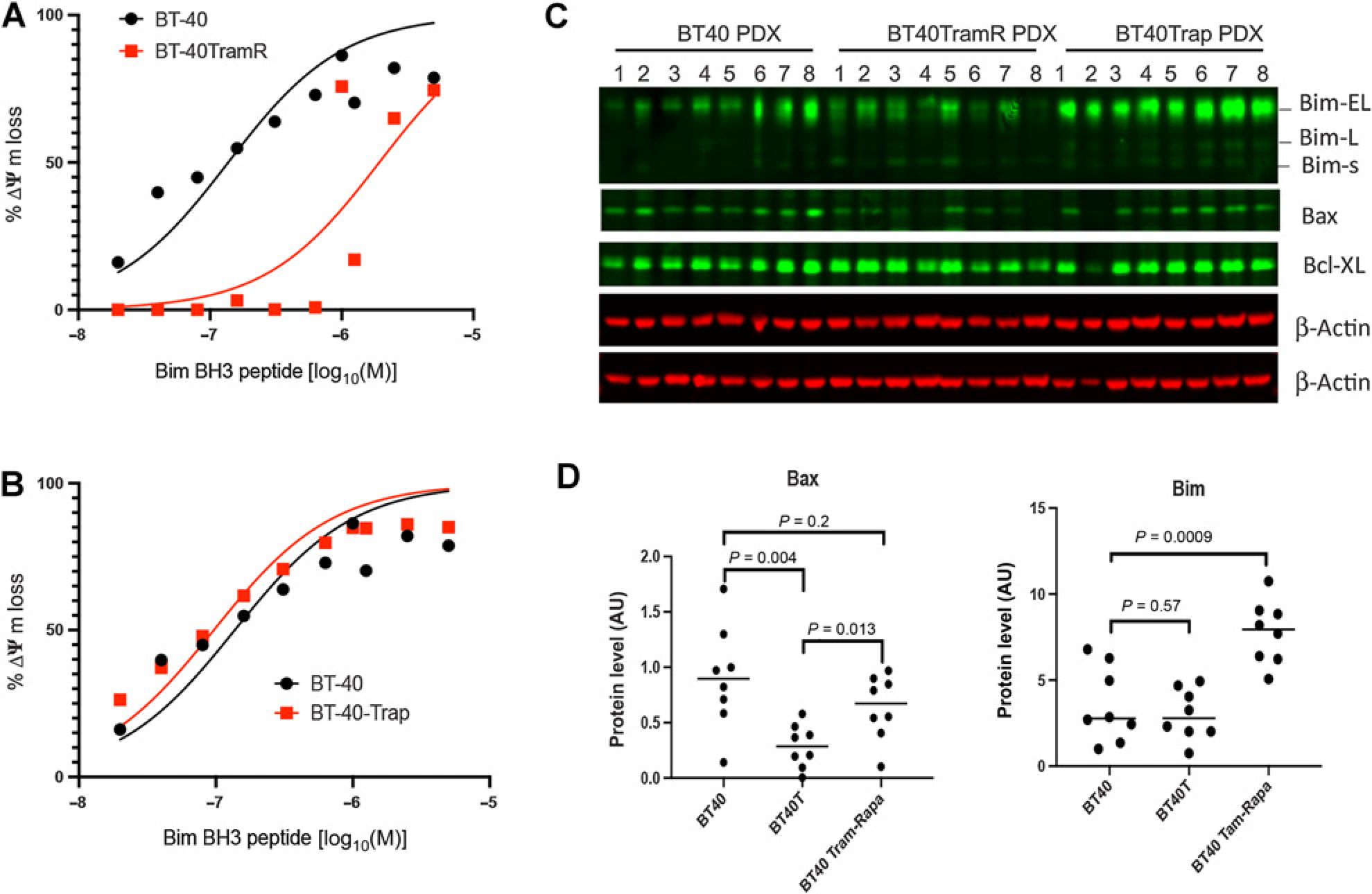
Trametinib resistance is associated with increased apoptotic threshold. A, Sensitivity of freshly isolated BT-40 or BT-40TramR (trametinib-resistant. Eight cycles of treatment in mice) and BT-40 Trap (trametinib–rapamycin—treated; 5 cycles in mice) cells to mitochondrial loss of membrane potential (Δψ) with increasing Bim BH3 peptide concentration; FCCP was used as a control to measure complete loss of membrane potential. ED50: BT-40 0.14 μmol/L [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.08–0.24 μmol/L]; BT-40TramR 1.94 μmol/L (95% CI, 0.91–4.5 μmol/L); BT-40Trap 0.1 μmol/L (95% CI, 0.04–0.15 μmol/L). B, Sensitivity of freshly isolated BT-40 or BT-40Trap cells (three cycles of trametinib + rapamycin in mice) to mitochondrial loss of membrane potential (Δψ) with increasing Bim BH3 peptide concentration; FCCP was used as a control to measure complete loss of membrane potential. C, Western blot for 8 BT-40 tumors and 8 trametinib-resistant PDX (TramR) and 8 trametinib—rapamycin–treated tumors (Trap) for Bax, Bim, and BCLXL; D, Quantitation of Bax and Bim levels from (C).
