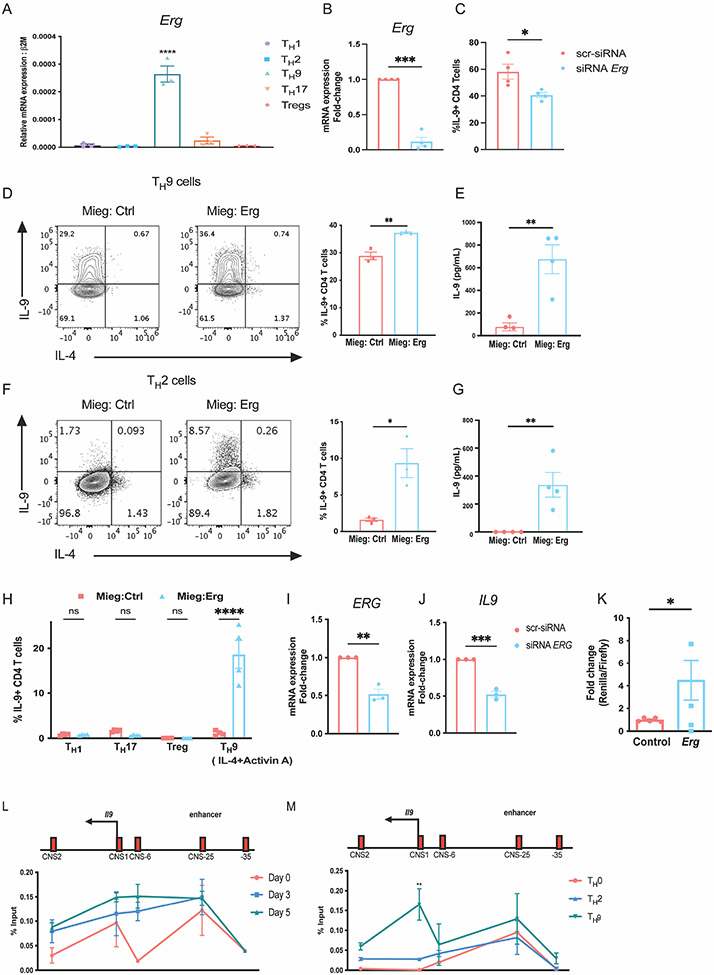
Figure 1: ERG promotes IL-9 production in murine and human CD4 T cells in vitro.
(A) Expression of Erg transcript in T-helper subsets. (B and C) SiRNA knock down of Erg in TH9 cells cultures in vitro showing, Erg expression and IL-9 production respectively. (D) IL-9 production in TH9 subsets after retroviral transductions of ERG overexpressing plasmid on day 1 of T cell differentiation in vitro. (E) Quantification of IL-9 protein secreted by TH9 cells overexpressing ERG. (F) IL-9 production in TH2 subsets after retroviral transductions of ERG overexpressing plasmid on day 1 of T cell differentiation in vitro. (G) Quantification of IL-9 protein secreted by TH2 cells overexpressing ERG. (H) IL-9 production in other T-helper subsets transduced with ERG overexpressing plasmid on day 1 of T cell differentiation in vitro. (I and J) ERG and IL9 transcript expression after siRNA-mediated knock-down of ERG in TH9 cells cultured in vitro from human PBMCs collected from healthy donors. (K) Il9 reporter activity measured as the ratio of Renilla/Luciferase with or without overexpression of Erg in Jurkat cells cultured in vitro. (L) ChIP-qPCR assay indicating ERG interactions at the Il9 regulatory regions in TH9 cells during differentiation through day 0, day 3 (expansion) and day 5. (M) ChIP-qPCR assay showing binding of ERG at Il9 regulatory regions on day 5 after re-stimulation with anti-CD3 antibody for 3 hours in TH9 cells compared TH0 and TH2 cells cultured in vitro. Data are mean of three-four mice or human PBMC donors per experiment and representative of two independent experiments. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001.