Figure 4.
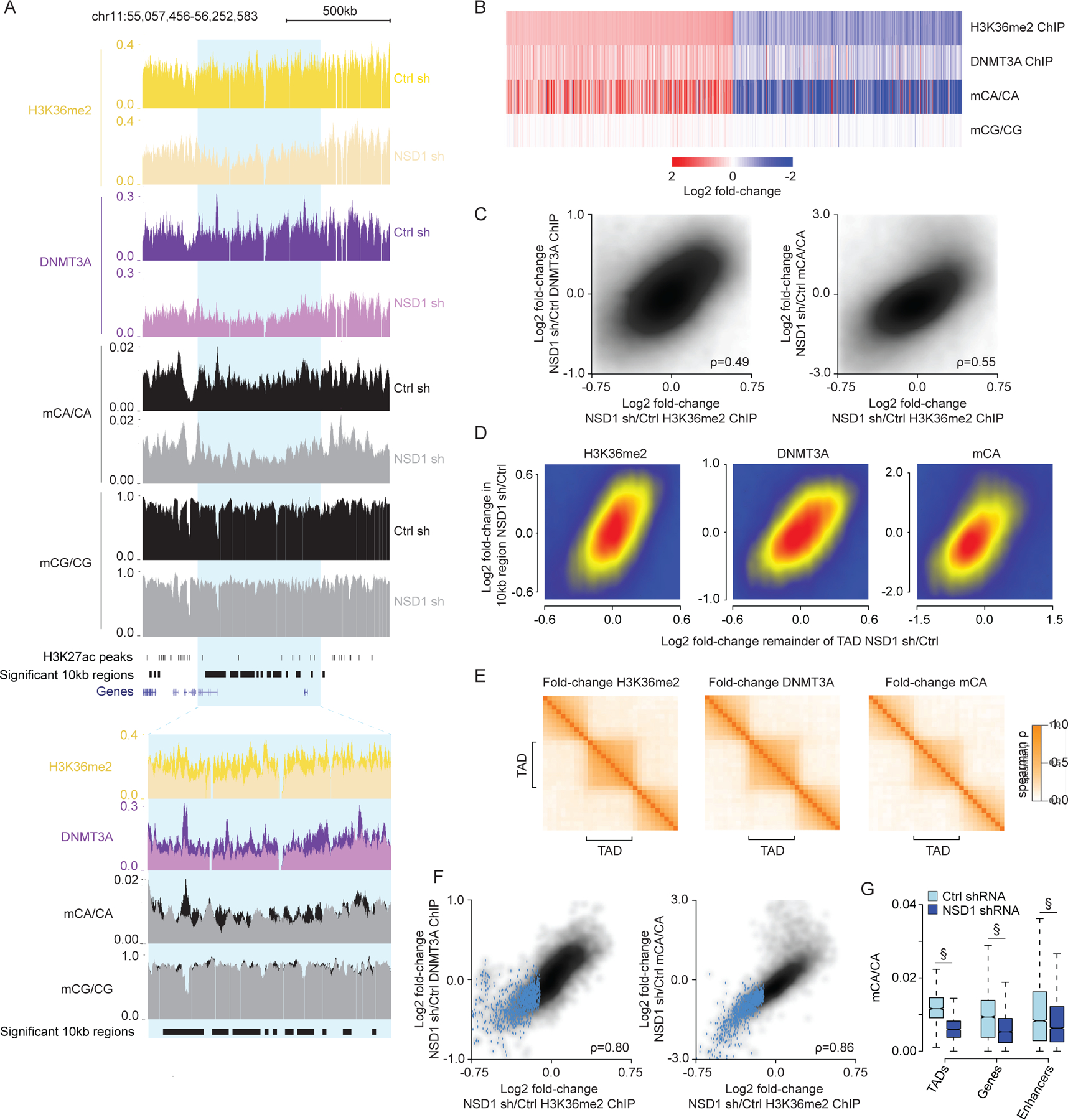
NSD1-mediated H3K36me2 is required for TAD-scale DNMT3A targeting and mCA deposition in postmitotic neurons.
(A) Genome browser view of DIV 12 ChIP-seq and DIV 18 DNA methylation from primary cortical neurons (PCN). Representative TAD with significantly reduced H3K36me2 upon NSD1 knockdown in blue. Overlap of multiple 10kb bins with significantly reduced H3K36me2 in this significantly altered TAD illustrates concordance of changed signals within TADs.
(B) Fold-changes of H3K36me2, DNMT3A, and DNA methylation in shNSD1 transduced PCNs at all 10kb regions identified by edgeR (FDR<0.1) as significantly altered for H3K36me2.
(C) Comparison of changes in H3K36me2 to changes in DNMT3A (left) or mCA (right) for 10kb regions genome-wide.
(D) Comparison of changes in H3K36me2, DNMT3A, or mCA between 10kb genomic regions and the TAD in which they reside.
(E) Cross-correlation analysis of fold-changes in H3K36me2, DNMT3A, and mCA upon NSD1 knockdown for regions inside and outside of TADs across the genome (see methods). Higher correlation of regions found within the same TAD compared to regions across TAD boundaries indicates regions within the same TAD are concordantly affected upon NSD1 loss.
(F) Comparison of changes in H3K36me2 to changes in DNMT3A or mCA for each TAD in the genome. TADs with significantly reduced H3K36me2 by edgeR (FDR<0.1) in blue.
(G) Boxplots of mCA levels in shCtrl and shNSD1 PCNs at TADs with significantly reduced H3K36me2 (edgeR, FDR <0.1) and kilobase-scale genomic elements that reside within these TADs. (§p < 10−15, Wilcoxon test).
Data are from PCNs transduced with shCtrl or shNSD1 on DIV 1 and collected at DIV 12 and DIV 18 for ChIP-seq and WGBS, respectively. Per time point: n = 2–4 bioreplicates for H3K36me2, DNMT3A ChIP, and DNA methylation. TADs are from Hi-C analysis of cortical neurons.59
