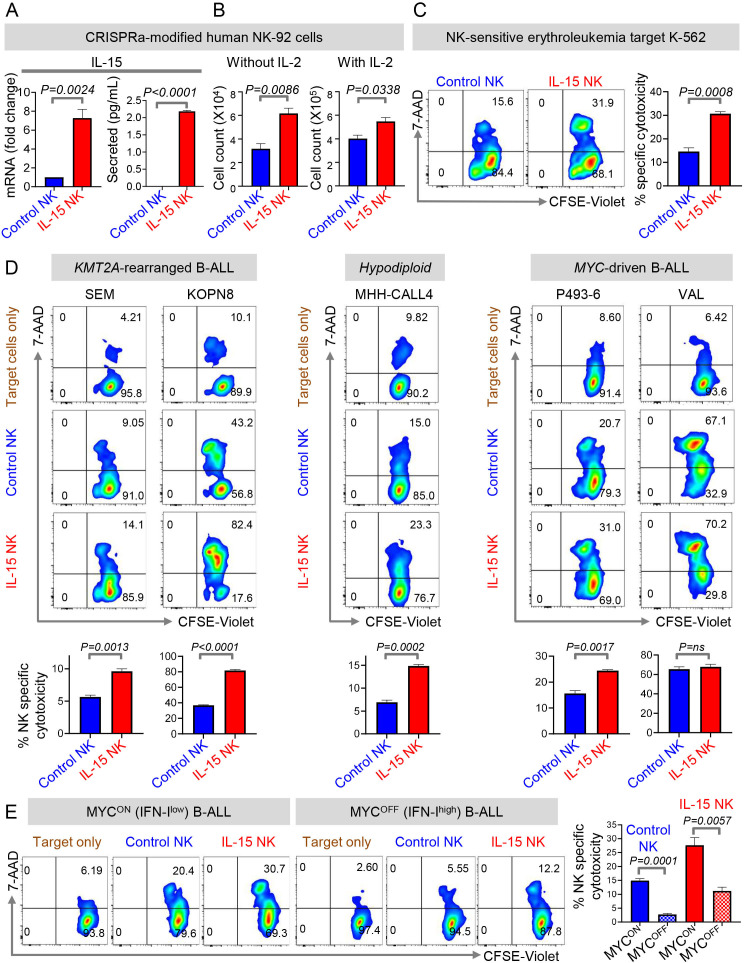
Figure 5.
CRISPRa-engineered IL-15 secreting NK cells eradicate MYC-overexpressing B-ALLs in vitro. (A)Fold change in IL-15 transcript levels by qPCR in dCas9-VP64-GFP+ NK-92 cells transduced with control sgRNA-RFP (Control NK) or IL-15 sgRNA-RFP (IL-15 NK) and levels of secreted IL-15 by ELISA in culture supernatant of control NK and IL-15 NK cells stimulated with PMA and Ionomycin for 24 hours. (B)Cell counts of control and IL-15 NK cells cultured in the presence and absence of rhIL-2 (100 U/mL) for 96 hours. (C, D)Specific cytotoxicity of control and IL-15 NK cells by flow cytometry using (C)K562, (D)SEM (KMT2A-rearranged), KOPN8 (KMT2A-rearranged), MHH-CALL4 (hypodiploid, CRLF2-rearranged), P493-6, and VAL as target cell lines. Effector: target=10:1. (E)Specific cytotoxicity of control and IL-15 NK cells by flow cytometry against MYC-overexpressing (MYCON) and MYC-inactivated (MYCOFF) P493-6 cells. MYC was inactivated by treatment of P493-6 cells with 0.2 µg/mL of doxycycline for 24 hours. p=0.0108, control (MYCON) vs IL-15 NK (MYCON); p=0.0037, control (MYCOFF) vs IL-15 NK (MYCOFF). All experiments were conducted in three technical and three biological replicates. One representative of three biological replicates of each experiment is shown. Comparisons between any two groups were conducted using Student’s t-test (A–E).Exact p values are provided whenever significant (<0.05) or trending to significance (0.05<p<0.1). B-ALL, B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia; NK, natural killer; ns, not significant.