FIG 2.
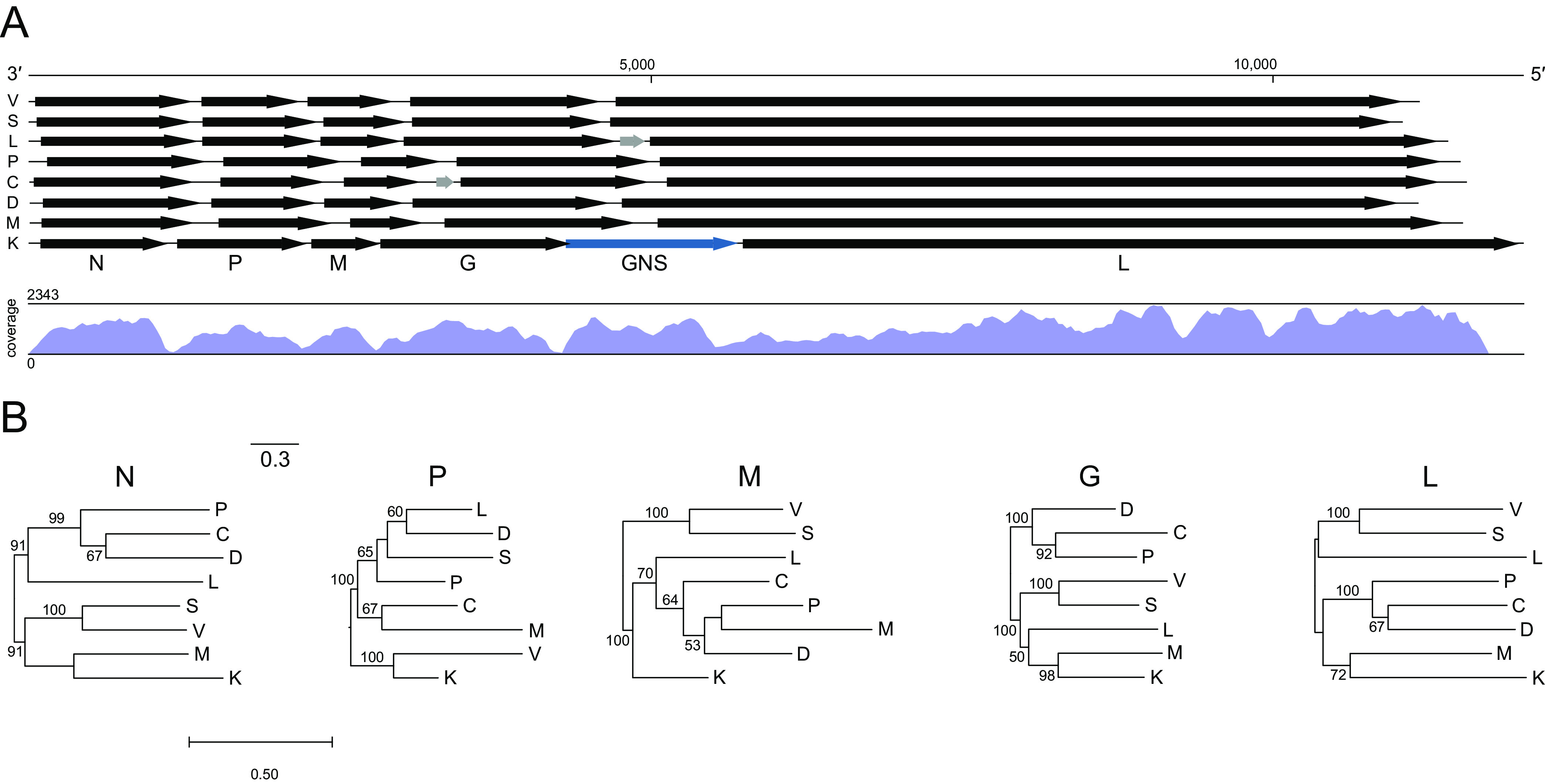
Genome organization, sequence coverage, and gene-specific phylogenies of killamcar virus 1 (KILLV-1) and exemplar viruses of seven genera within the subfamily Alpharhabdovirinae. Viruses are Siniperca chuatsi rhabdovirus (C; Siniperhavirus), dolphin rhabdovirus (D; Cetarhavirus), Le Dantec virus (L; Ledantevirus), Scophthalmus maximus rhabdovirus (M; Scophrhavirus), perch rhabdovirus (P; Perhabdovirus), spring viremia of carp virus (S; Sprivivirus), vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus (V; Vesiculovirus), and KILLV-1 (K; currently unassigned) (Table S1). Arrows (A) indicate open reading frames (scale = nucleotides). Black arrows indicate canonical rhabdovirus gene ORFs in the order nucleoprotein (N), phosphoprotein (P), matrix (M), glycoprotein (G), and RNA-directed RNA polymerase (L); gray arrows indicate accessory genes; and blue arrow indicates the KILLV-1 duplicated glycoprotein gene (GNS). Letters beneath ORFs refer to KILLV-1. Map shows coverage of the KILLV-1 genome. Maximum likelihood phylogenies (B) are shown for each of the canonical rhabdoviral gene ORF nucleotide sequences. Bootstrap values above branches are based on 1,000 replicates (only values ≥50% are shown). Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
